Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ICSE-CALORIMETRY-EXERCISE-11(B) (NUMERICALS)
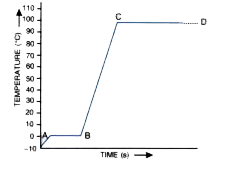
- A piece of ice is heated at a constant rate. The variation in temperat...
Text Solution
|
- 10 g of ice at 0°C absorbs 5460 J of heat energy to melt and change to...
Text Solution
|
- How much heat energy is released when 5.0 g of water at 20^@C changes ...
Text Solution
|
- A molten metal of mass 150 g is kept at its melting point 800^@C. When...
Text Solution
|
- A solid metal weighing 150 g melts at its melting point of 800^(@)C by...
Text Solution
|
- A refrigerator converts 100 g of water at 20^@C to ice at - 10^@C in 7...
Text Solution
|
- In an experiment, 17 g of ice is used to bring down the temperature of...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature of 170 g of water at 50^@C is lowered to 5^@C by addin...
Text Solution
|
- Find the result of mixing 10 g of ice at -10^@C with 10 g of water at ...
Text Solution
|
- A piece of ice of mass 40 g is added to 200 g of water at 50^@C. Calcu...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the mass of ice needed to cool 150 g of water contained in a...
Text Solution
|
- 250 g of water at 30^(@)C is present in a copper vessel of mass 50 g. ...
Text Solution
|
- How much boiling water at 100^@C is needed to melt 2 kg of ice so that...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the total amount of heat energy required to convert 100 g of...
Text Solution
|
- The amount of heat energy required to convert 1 kg of ice at -10^@C to...
Text Solution
|
- 200 g of ice at 0^@C converts into water at 0^@C in 1 minute when heat...
Text Solution
|