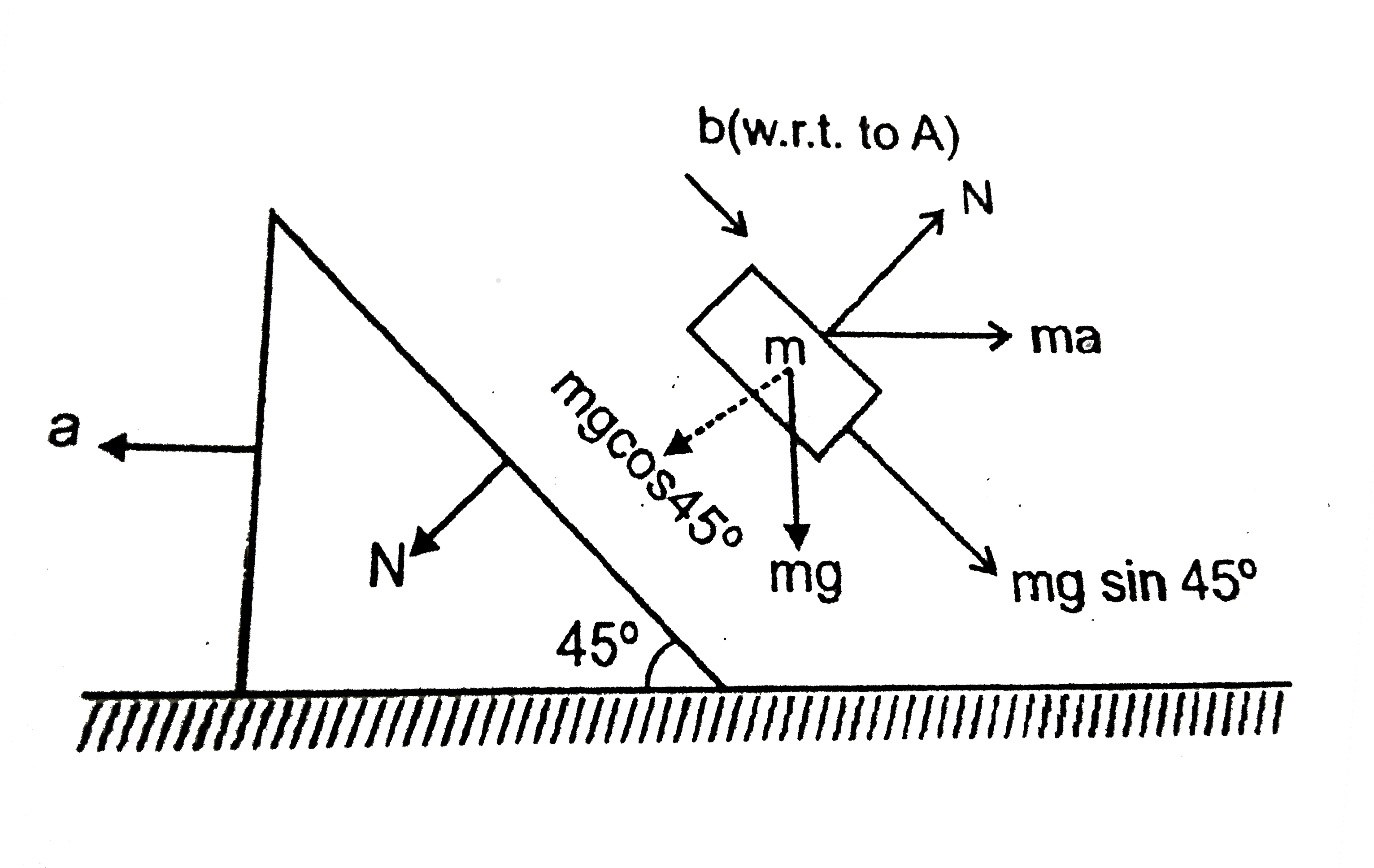A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp29|5 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 30|4 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 27|3 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise|53 VideosELASTICITY AND VISCOCITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Advanced Level Problems|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS-dpp 28
- Two stones A and B are projected from an inclined plane such that A ha...
Text Solution
|
- A man is moving downward on an inclined plane (theta=37^(@)) with velo...
Text Solution
|
- System is shown in the figure. Velocity of sphere A is 9m//s . Then sp...
Text Solution
|
- Two beads A and B of equal mass m are connected by a light inextensibe...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown all the surface are smooth. All the blocks A,B and...
Text Solution
|
- A block B of mass 0.6kg slides down the smooth face PR of a wedge A of...
Text Solution
|
- Find the tension in the string and the extension in the spring at equi...
Text Solution
|