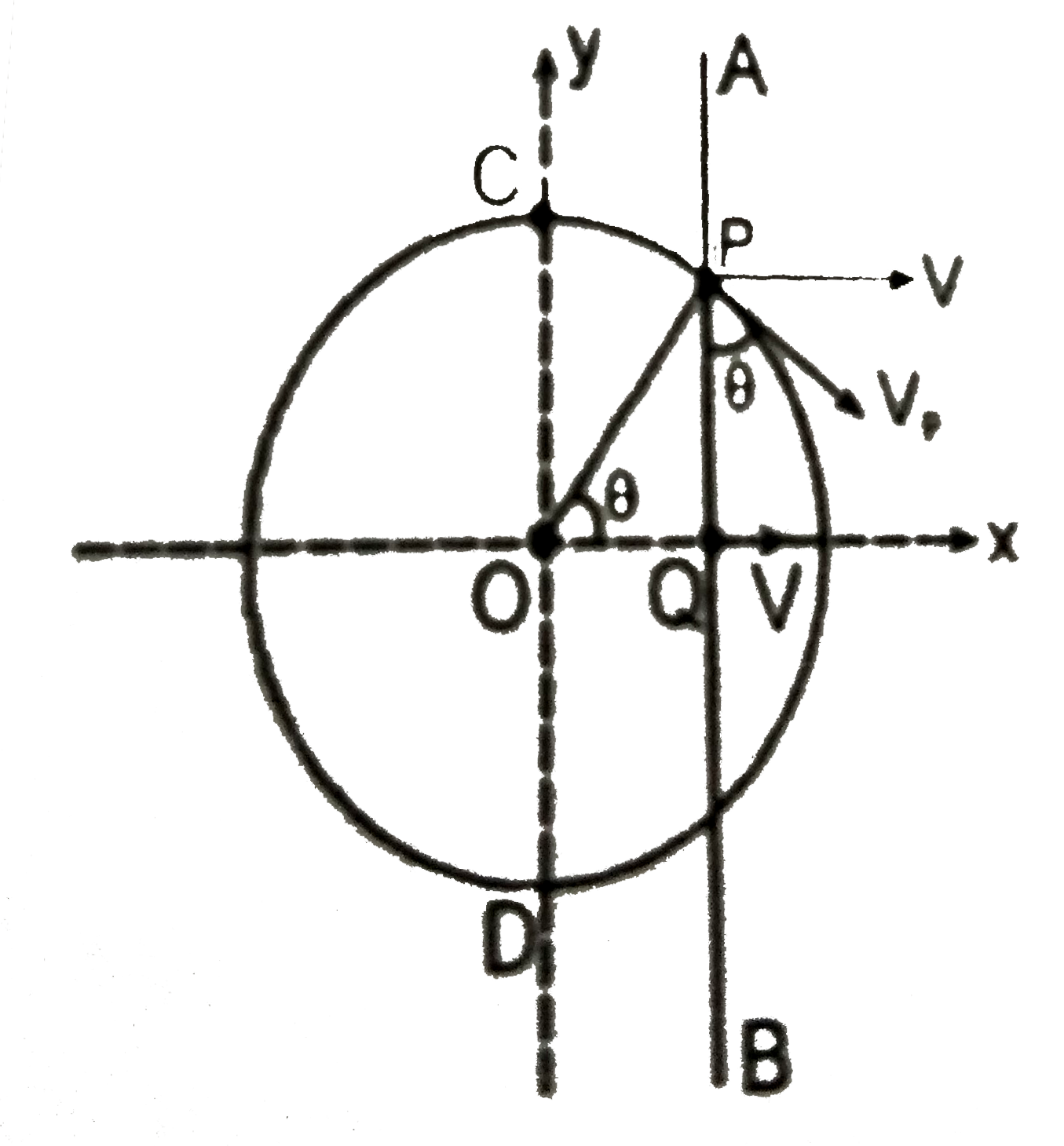
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 64|5 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise DPP 65|5 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise DPP 62|4 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise|53 VideosELASTICITY AND VISCOCITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Advanced Level Problems|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS-dpp 63
- A uniform disc of mass m and radius r and a point mass m are arranged ...
Text Solution
|
- Mass m is connected with an ideal spring of natural length l whose oth...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m is attached to the lower end of a light vertical spri...
Text Solution
|
- A rod AB is moving on a fixed circle of radius R with constant velocit...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform beam of length L. And mass m is supported as shown. Of the c...
Text Solution
|