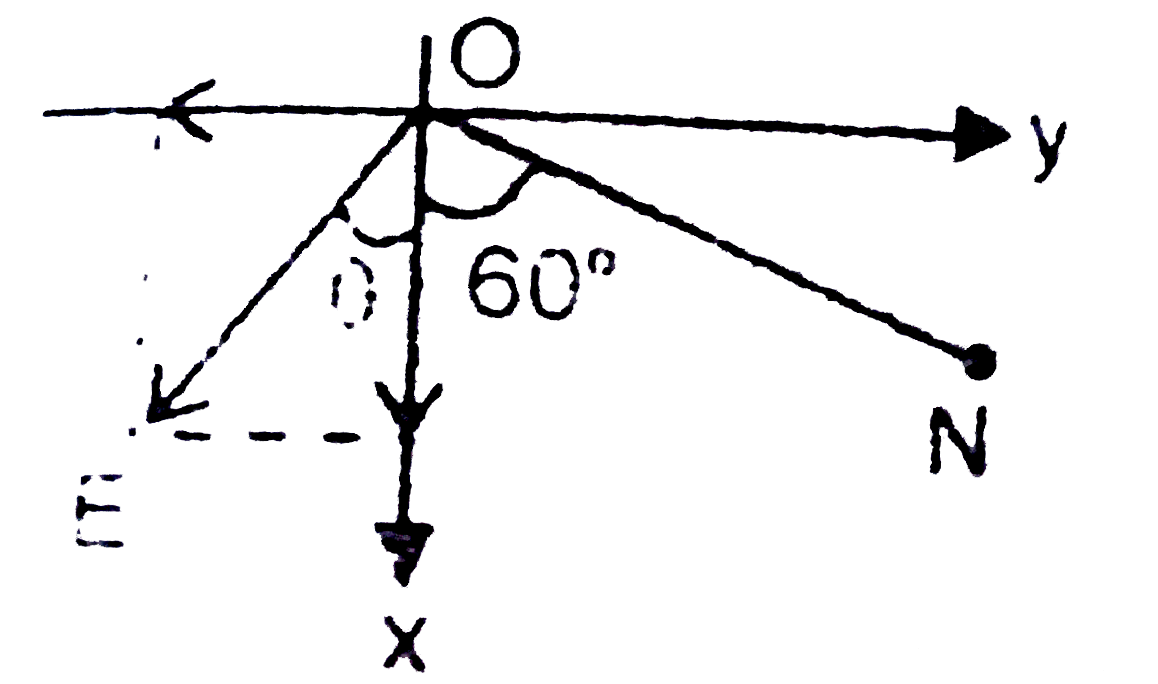
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise DPP No.38|20 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise DPP No.39|9 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise DPP No.36|20 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise High Level Problems (HIP)|19 VideosELECTRO MAGNETIC WAVES
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 3|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM-DPP No.37
- In the figure shown : (All batteries are ideal)
Text Solution
|
- In a system of two dipoles placed in the way as shown in figure :
Text Solution
|
- In the shown circuit
Text Solution
|
- The switch shown in figure is suddenly closed. Find the current throug...
Text Solution
|
- AB and CD are two uniform resistance wires of lengths 100 cm and 80 cm...
Text Solution
|
- A solid uniform cylinder of mass m performs small oscillations due to ...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field intensity at all points in space is given by vecE=s...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field intensity at all points in space is given by vec(E)...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field intensity at all points in space is given by vecE =...
Text Solution
|