A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-FLUID MECHANICS-Advanced Level Problems
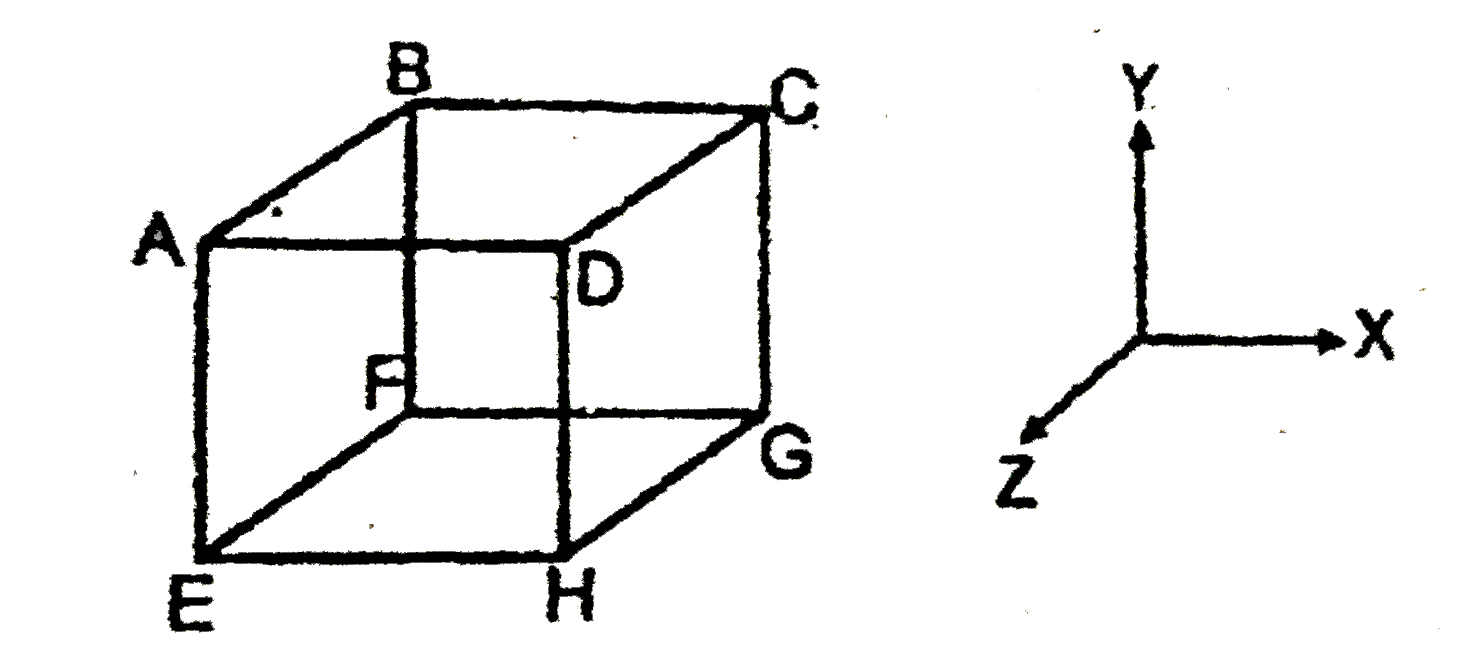
- The cubical container ABCDEFGH which is completely filled with an idea...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of density d is dropped onto a horizontal solid surface. It bou...
Text Solution
|
- Two cyllindrical vessels of equal cross sectional ara A contain water ...
Text Solution
|
- A wooden stick of length L, radius R and density rho has a small metal...
Text Solution
|
- A container of large uniform cross-sectional area A resting on a horiz...
Text Solution
|
- A container of cross-section area 'S' and height 'h' is filled with m...
Text Solution
|
- A Pitot tube is shown in figure. Wind blows in the direction shown. Ai...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a long iron chain of linear mass density lambda is fixed to...
Text Solution
|
- Two very large open tanks A & F both contain the same liquid. A horizo...
Text Solution
|