Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-NUCLEAR PHYSICS-Exercise -3 Part-III CBSE PROBLEMS (LAST 10 YEARS)
- A neutron is absorbed by a .(3)^(6)Li nucleus with the subsequent emis...
Text Solution
|
- What do you understand by isotopes, isobars and isotones? Explain with...
Text Solution
|
- The nucleus ""(10)^(23) Ne decays by beta– emission. Write down the ...
Text Solution
|
- Two nuclei have mass numbers in the ratio 1 : 2. What is the ratio of ...
Text Solution
|
- A radioactive nucleus undergoes a series of deacy according to the sch...
Text Solution
|
- Name and define, the SI unit for the 'activity' of a given sample of r...
Text Solution
|
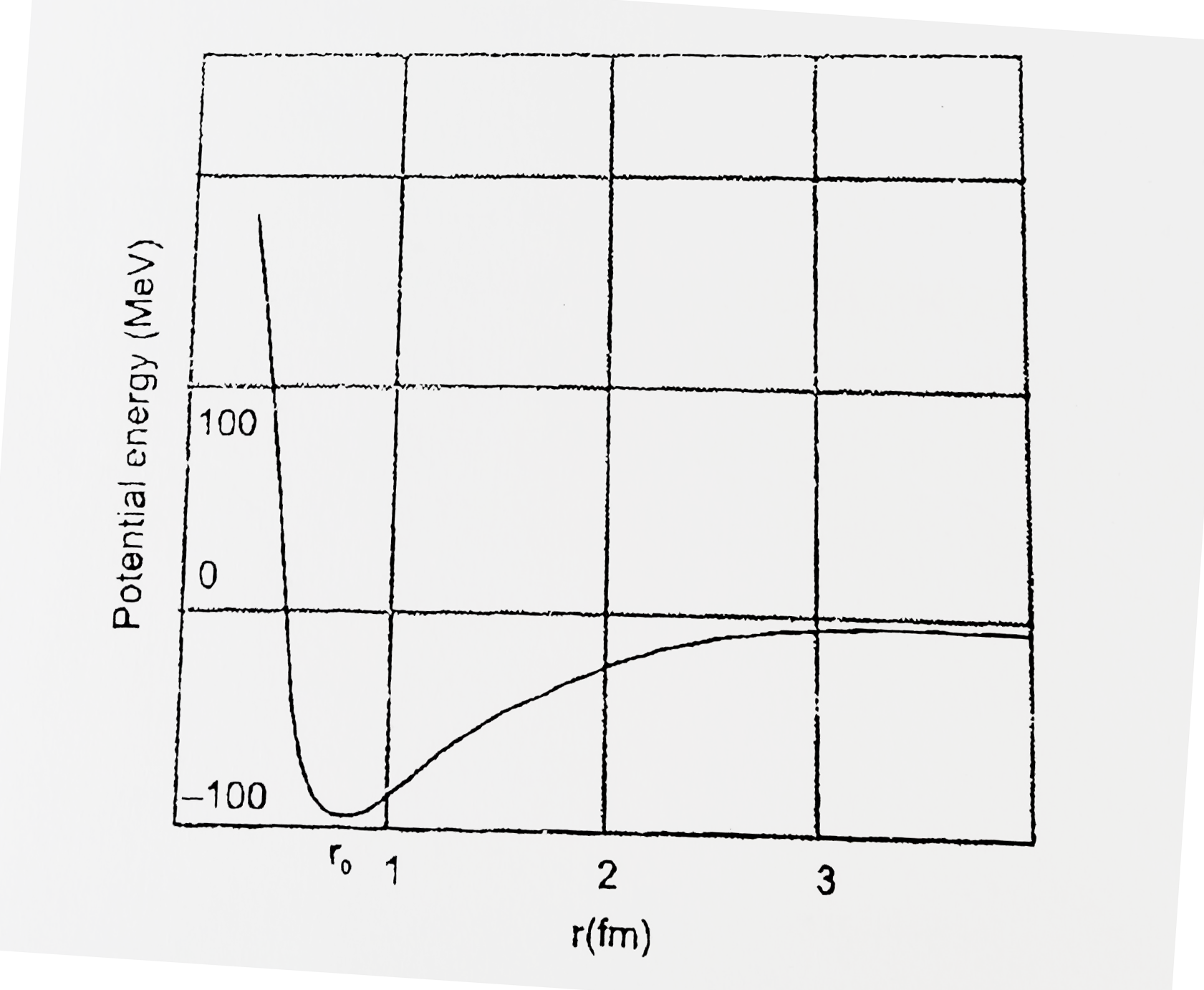
- Draw a plot of potential energy of a pair of nucleons as a function of...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Write symbolically the beta-decay process of ""(15)^(32)P. (b) ...
Text Solution
|
- How is the size of nucleus experimentally determined ? Write the relat...
Text Solution
|
- State the law of redioactive decay. Plot a graph showing the number (N...
Text Solution
|
- What is the effect on neutron to proton ratio in a nucleus when (i) an...
Text Solution
|
- A nucleus undertgoes beta-decay. How does its (i) mass number (ii) at...
Text Solution
|
- How are the radius of nucleus r and mass number (A) related to each ot...
Text Solution
|
- For radioactive disintegration of a radioactive substance, show that ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Why photoelectric effect cannot be explained on the basis of wave ...
Text Solution
|
- An element A decays into an element C by a two step process A to B + ....
Text Solution
|
- Write the law of radioavtive decay. Decay constant of a radioactive su...
Text Solution
|
- For the past some time, Aarti had been observing some erratic body mov...
Text Solution
|
- The decay constant of a radioactive substance is 0.693 per minute. Wha...
Text Solution
|
- From the relation R=R(0)A^(1//3) where R(0) is a constant and A is the...
Text Solution
|