Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
BIOMOLECULES
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Advanced Level(Part I)|20 VideosBIOMOLECULES
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Advanced Level(Part II)|33 VideosBIOMOLECULES
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Ex-3(IIT-JEE)Part-II|15 VideosBASIC CONCEPTS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(BASIC CONCEPTS)|27 VideosBIOMOLECULES & POLYMER
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(Biomolecules & Polymer)|34 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-BIOMOLECULES-Ex-3(IIT-JEE)Part-III
- In which classes, the polymers are classified on the basis of molecula...
Text Solution
|
- What is the effect of denaturation on the structure of proteins?
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the main purpose of vulcanisation of rubber
Text Solution
|
- Differentiate between globular and fibrous proteins.
Text Solution
|
- What is the difference between a nucleoside and a nucleotide?
Text Solution
|
- Find rms speed of Cobalt molecules at temperature 27^(@)C.
Text Solution
|
- If rate of diffusion of A is 4 times that of B, what will be the densi...
Text Solution
|
- Enumerate the reactions of D-glucose which cannot be explained by its ...
Text Solution
|
- How are vitamins classified? Name the vitamin responsible for the coag...
Text Solution
|
- Define thermoplastics and thermosetting polymers with two examples of ...
Text Solution
|
- What are the monomeric repeating units of Nylon-6 and Nylon-6,6?
Text Solution
|
- Find rms speed of Potassium molecules at temperature 27^(@)C.
Text Solution
|
- What is a glycosidic linkage?
Text Solution
|
- What are the expected products of hydrolysis of lactose ?
Text Solution
|
- What are reducing sugars?
Text Solution
|
- If rate of diffusion of A is 3 times that of B, what will be the densi...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following terms: (i) Invert sugar (ii) Polypeptides
Text Solution
|
- Name the products of hydrolysis of sucrose. Why sucrose is not a reduc...
Text Solution
|
- Give one example each of (i) addition polymers, (ii) condensation ...
Text Solution
|
- What does the designation '6,6' mean in the name nylon-6,6 ?
Text Solution
|
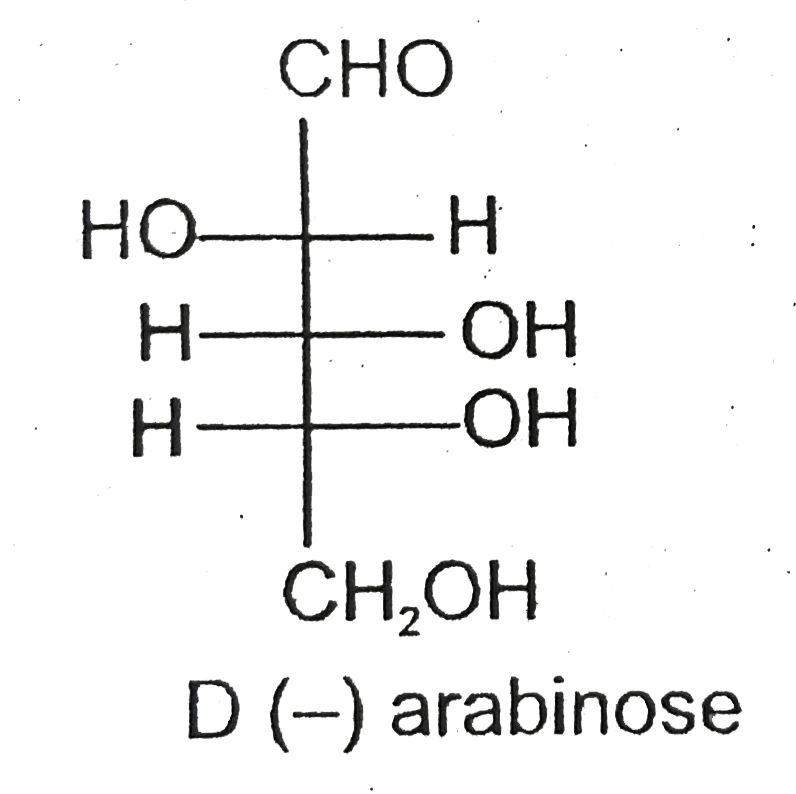 .
.