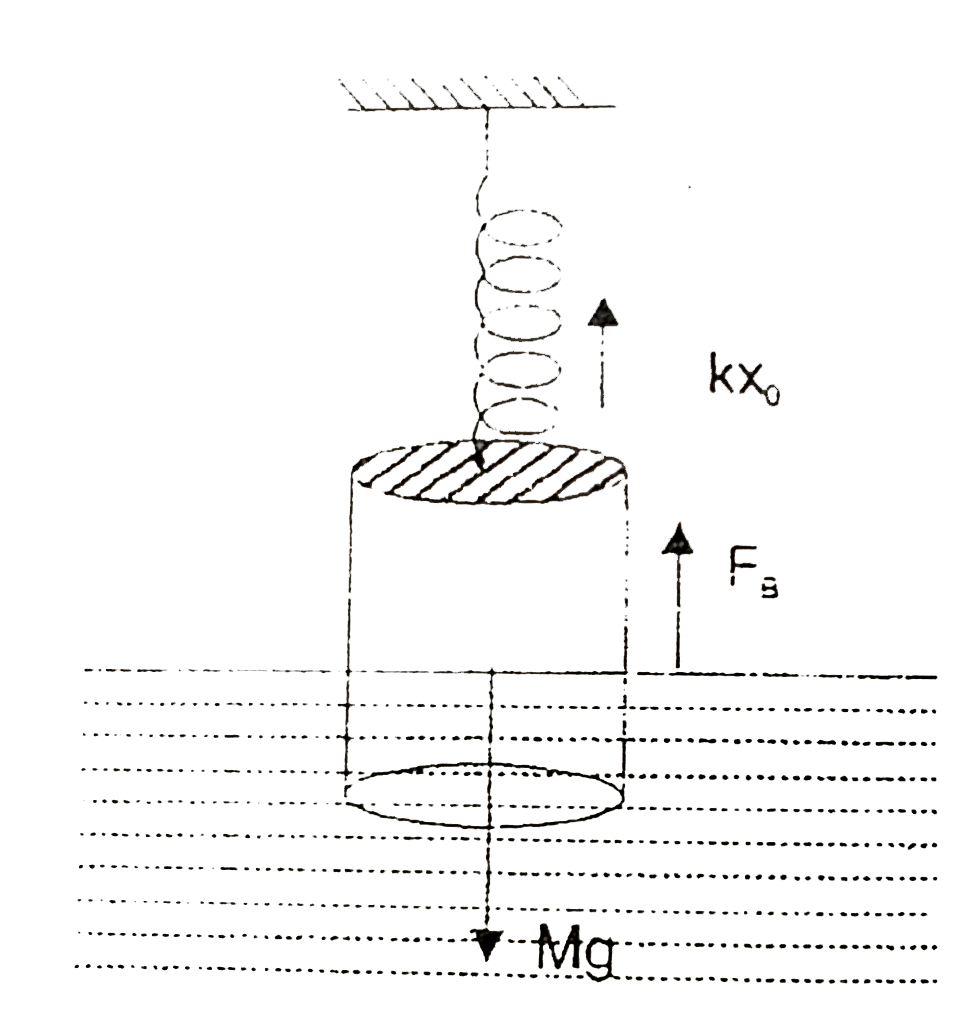
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-FLUID MECHANICS-Exercise- 3 PART - II
- A jar filled with two non mixing liquids 1 and 2 having densities rho(...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is made of a material of density rho where rho(oil) lt rho lt r...
Text Solution
|
- Water is flowing continuously from a tap having an internal diameter 8...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform cylinder of length L and mass M having cross-sectional area ...
Text Solution
|
- There is a circular tube in a vertical plane. Two liquids which do not...
Text Solution
|