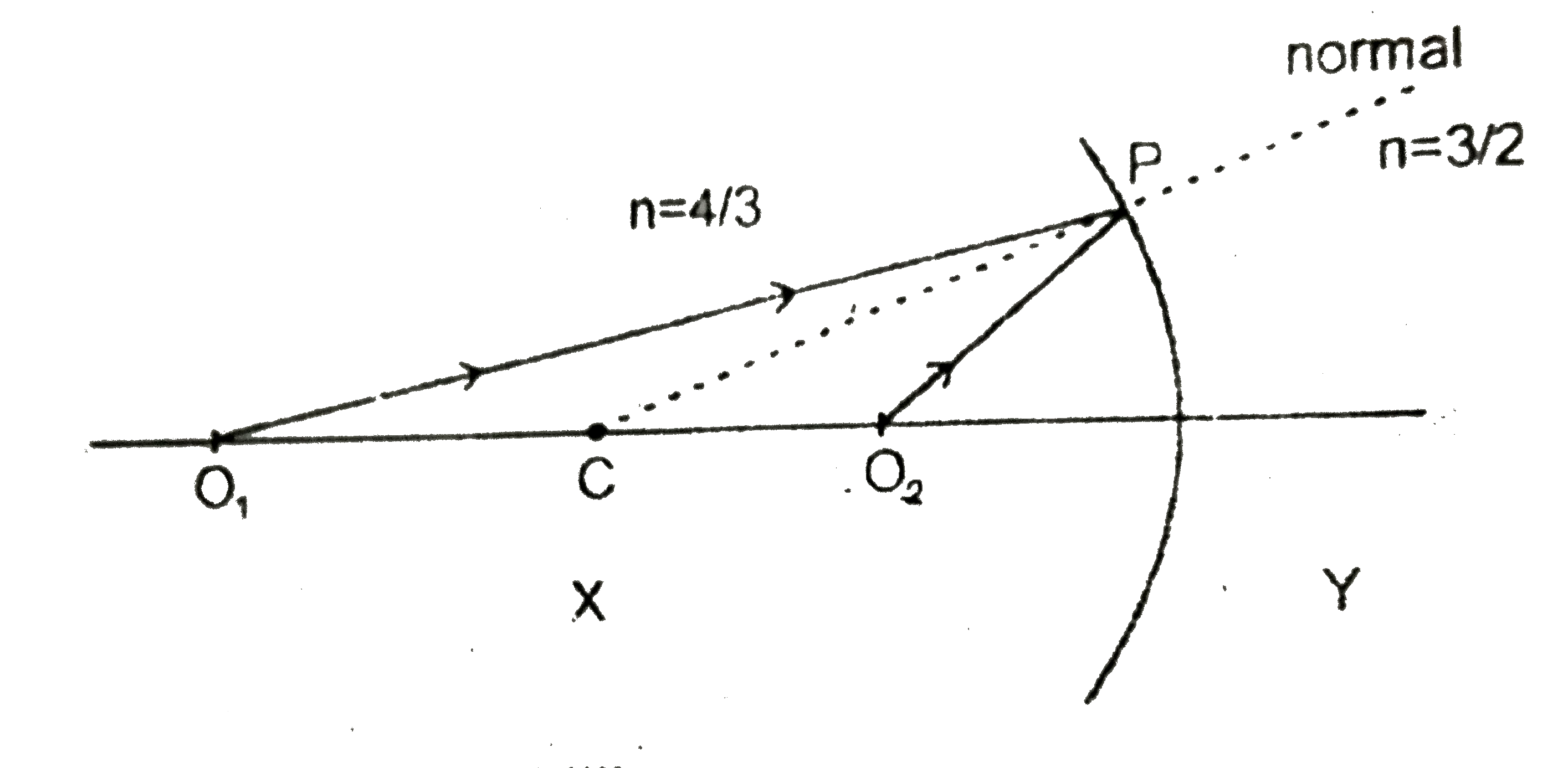
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-TEST PAPERS-PHYSICS
- Two point objects are placed on principal axis of a thin converging le...
Text Solution
|
- Inside a solid glass sphere of radius R, a point source of light lies ...
Text Solution
|
- A concave spherical surface of radius of curvature 10 cm separates two...
Text Solution
|
- Choose the most appropriate graph of i(min)v//s A, for a light ray whi...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal light ray passes through a prism (mu=1.5) of angle 4^(@)....
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a object placed in front of a lens of focal length 10 cm,...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens is cut into two parts in different ways that are arrange...
Text Solution
|
- The magnifying power of a telescope can be increased
Text Solution
|
- A red postage stamp is viewed in yellow (monochromatic) light. It appe...
Text Solution
|
- In a compound microscope
Text Solution
|
- An electromagnetic wave travelling through a transparent medium is giv...
Text Solution
|
- Two light waves travelling in same medium are given by E(1)=2sin(100pi...
Text Solution
|
- If young's double slit experiment is performed in water
Text Solution
|
- A point object is placed at a distance 20 cm from the focus of a conca...
Text Solution
|
- A small wooden rod of length 5mm is fixed at the bottom of the contain...
Text Solution
|
- A ray is incident on a sphere of refractive index sqrt(2) as shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- If the distance between two images formed by upper and lower part of t...
Text Solution
|
- The minimum magnifying power of a telescope is M. If focal length of i...
Text Solution
|
- The dispersive power of the material of a lens is 0.04 and the focal l...
Text Solution
|
- A thin prism of glass is placed in air and water respectively. If n(0)...
Text Solution
|