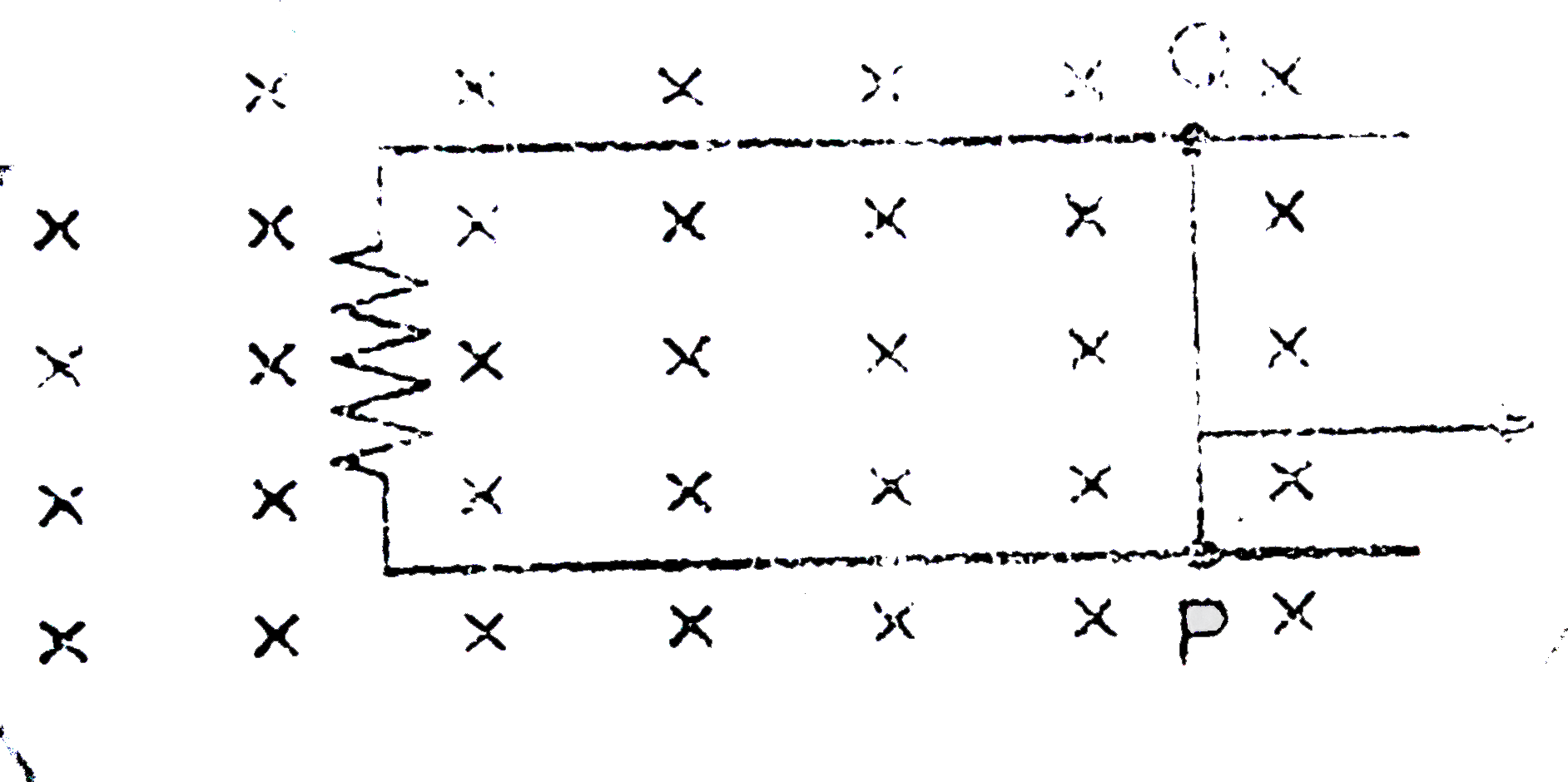Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-Exercis-3 PART 3
- A mercury drop of radius 1 cm is sprayed into 10^(6) droplets of equal...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Define self inductance. Write its S.I. units (b) Derive and expr...
Text Solution
|
- Define magnetic flux . Give its SI unit. I
Text Solution
|
- A 0.5m long metal rod PQ completes the circuit as shown in the figure...
Text Solution
|
- (a) State Lanz's law. Give one example to illustrate this law. "The Le...
Text Solution
|
- A plot of magnetic flux (phi) versus current (I) is shown in the fiugr...
Text Solution
|
- Describe briefly, with the help of a labell diagram, the basic element...
Text Solution
|
- State Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. Figure shows a rec...
Text Solution
|
- A current is induced in coil C1 due to the motion of current carrying...
Text Solution
|
- A bar magnet is moved in the direction indicated by the arrow between...
Text Solution
|
- State Lenz's Law. A metallic rod held horizontally along east-west...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of length 'I' is rotated with a frequency v with one e...
Text Solution
|
- Write Faraday,s law of electronmagnetic induction.
Text Solution
|
- (a) A rod of length l is moved horizontal with a uniform velocity v in...
Text Solution
|
- A bar magnet NS is moved in the direction indicated by an arrow betwee...
Text Solution
|
- Two concentric circular coils of radius r and R are placed coaxially w...
Text Solution
|