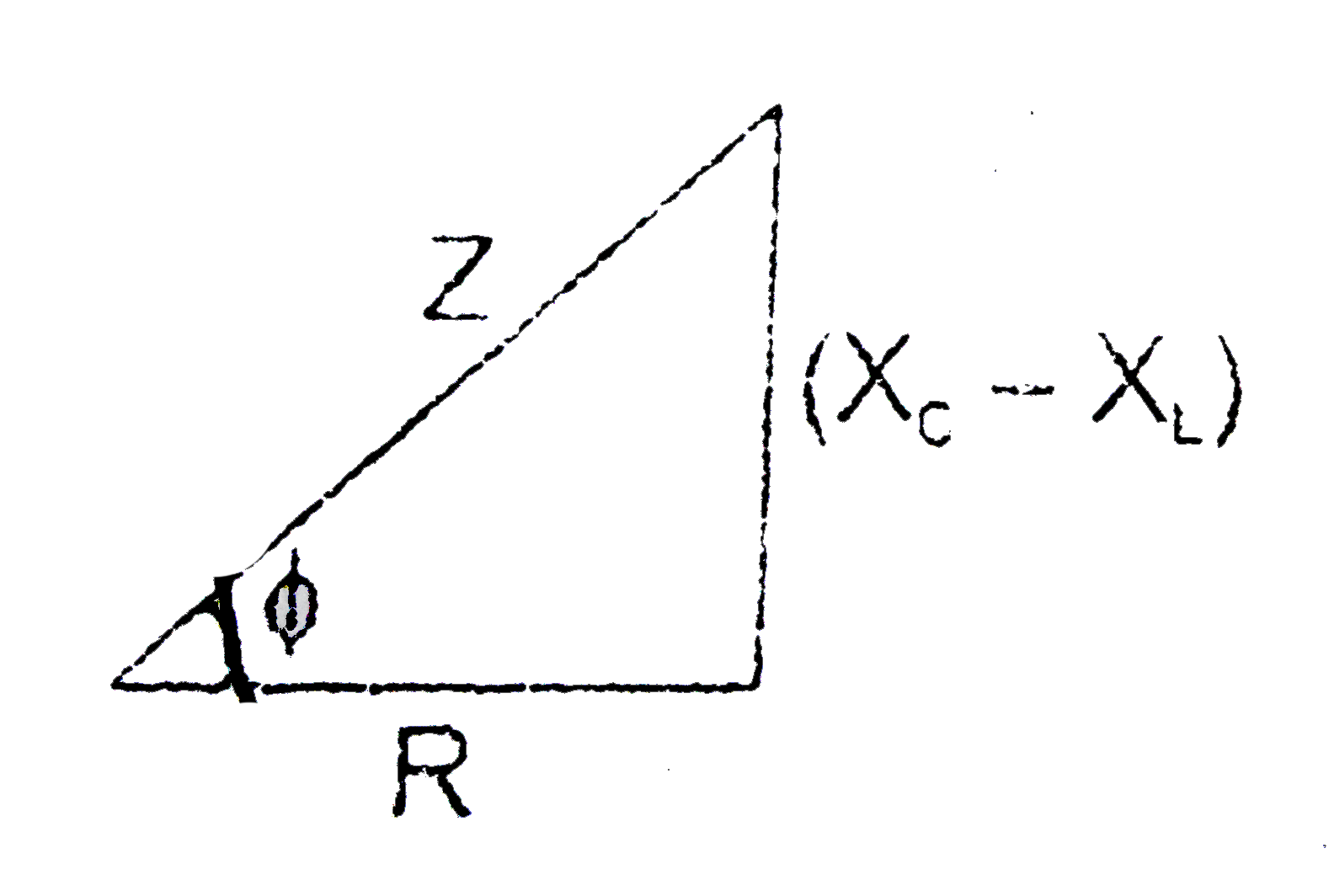Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-ALTERNATING CURRENT-Exercise -3 Part-3
- What do you mean by the impedance of LCR-circuit
Text Solution
|
- The instantaneous current from an a.c. source is l = 5 sin (314t) ampe...
Text Solution
|
- (i) with the help of a labelled diagram, describe briefly the underly...
Text Solution
|
- Given below are two electric circuits A and B Calculate the ratio of...
Text Solution
|
- In a series LCR circuit, the voltages across an inductor, a capacitor ...
Text Solution
|
- The current drawn by the primary of a transformer, which steps down 20...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the term 'inductive reactance'.Show graphically the variation ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the term 'capacitive reactance'.Show graphically the variation...
Text Solution
|
- Derive an expression for the impedance of an a.c. circuit consisting...
Text Solution
|
- An inductor 200 mH, capactior 500 mu F, resistor 10 ohm are connected ...
Text Solution
|
- The instantaneous current and voltage of an a.c. circuit are given by ...
Text Solution
|
- A coil Q is connected to low voltage bulb B and placed near another co...
Text Solution
|
- A series LCR circuit is connected to an ac source having voltage v=v(m...
Text Solution
|
- In a series LCR circuit connected to an ac source of variable frequenc...
Text Solution
|
- In an alternating circuit applied voltage is 200V, if R=8W X(L)=X(C)=6...
Text Solution
|
- Derive the expression for the instantaneous value of the emf induced ...
Text Solution
|
- Why is the use of A.C. voltage preferred over D.C. voltage? Give two r...
Text Solution
|
- A voltage V = V(0)sinomegat is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive...
Text Solution
|
- In an alternating circuit applied voltage is 200V if R=8W X(L)=X(C)=6O...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a curve for showing variation in alternating current with frequen...
Text Solution
|