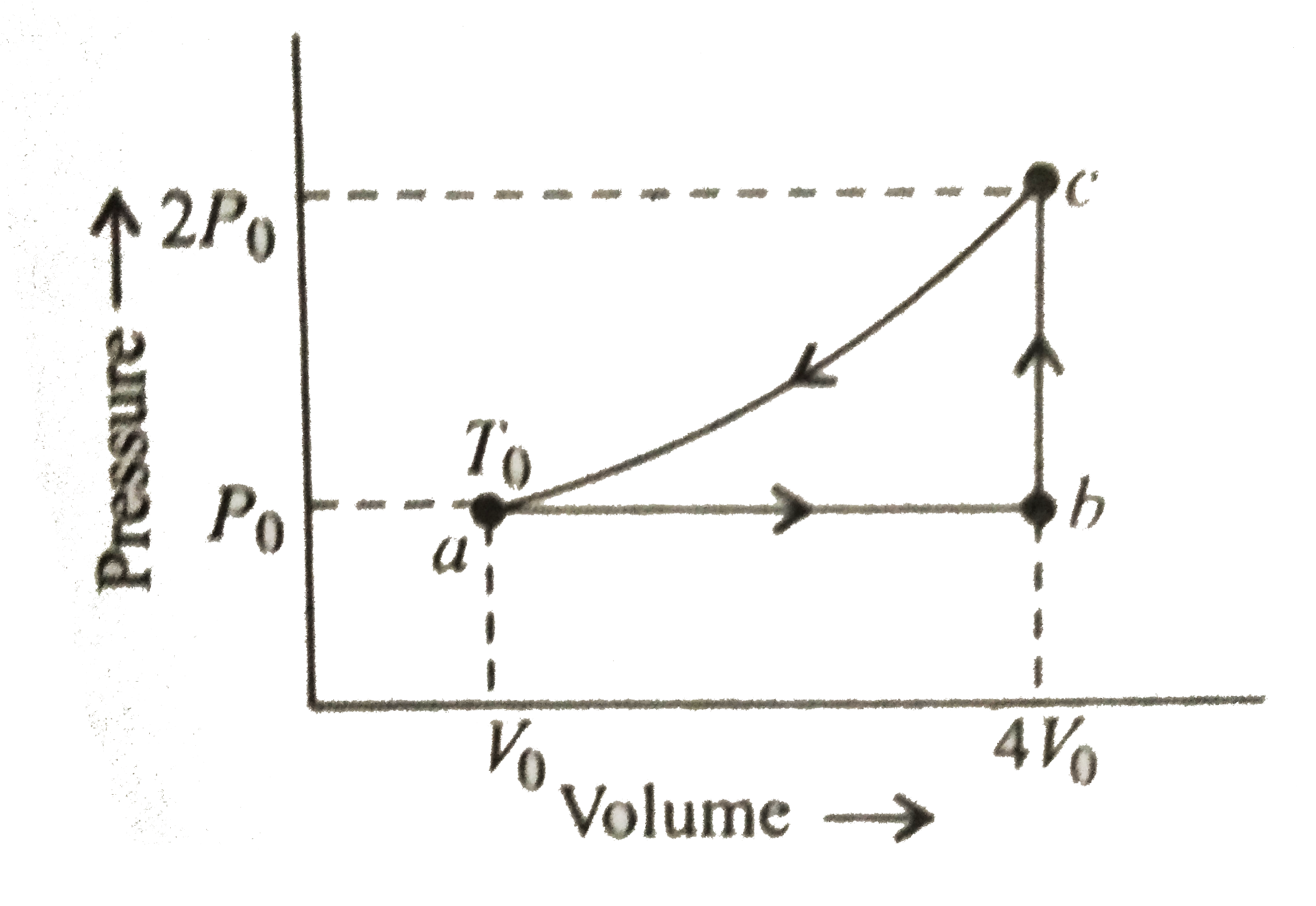
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-THERMODYNAMICS-MISCELLANEOUS SOLVED EXAMPLES
- Find (in terms of 'a') the amount of energy required to raise the temp...
Text Solution
|
- A thermally isolated vessel contains 100g of water at 0^(@)C. When air...
Text Solution
|
- Work done in expansion of an ideal gas from 4 litre to 6 litre against...
Text Solution
|
- 1 mole of ice at 0^(@)C and 4.6 mm Hg pressure is converted to water v...
Text Solution
|
- For Ag, bar(C)(p)(JK^(-1)mol^(-1)) is given by 24+0.006 T. Calculate D...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the amount of heat evolved during the complete combustion of...
Text Solution
|
- DeltaG for the reaction : (4)/(3) Al+O(2)rarr (2)/(3)Al(2)O(3) is...
Text Solution
|
- The standard molar enthalpies of formation of cyclohexane (I) and benz...
Text Solution
|
- Following graph shows a single stange expansion process, then workdone...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of 2kg of helium (assumed ideal) is taken through the process...
Text Solution
|
- In an isothermal expansion of a gaseous sample the correct relation is...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal mono-atomic gas is caused to go through the cycle...
Text Solution
|
- A certain gas in expanded from (1L, 10 atm) to (4L, 5 atm) against a c...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas expands isothermally against const...
Text Solution
|
- For a perfectly crystalline solid C(p,m)=aT^(3), where a is constant. ...
Text Solution
|
- Given the following data {:("Substance",DeltaH^(@)(KJ//mol),S^(@)(J/...
Text Solution
|
- If Delta H(f)^(@) for Ag^(+) (infinitely diluted), NO(3)^(-) (infinite...
Text Solution
|
- What is the work done against the atmosphere when 25 grams of water va...
Text Solution
|