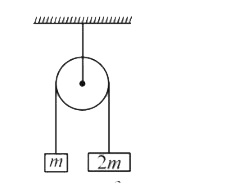
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-JEE MAIN REVISION TEST- 24 -PHYSICS ( SECTION - 2)
- A string of length and mass per unit length is used in atwood mach...
Text Solution
|
- A carnot engine takes 300 cal. of heat at 500 k and rejects 150 cal o...
Text Solution
|
- The real coefficient of volume expansion of glycerine is 0.000597per^(...
Text Solution
|
- A particle (m = 1kg) slides down a frictionless track (AOC) starting f...
Text Solution
|
- A loop made of straight edegs has six corners at A(0,0,0), B(L, O,0) C...
Text Solution
|
- Monochromatic light of wavelength 3000 Å is incident normally on a su...
Text Solution
|