Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-JEE MAIN REVISION TEST - 26 (2020)-PHYSICS (SECTION 2)
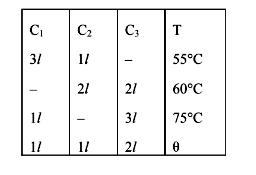
- Three containers C(1) , C(2) and C(3) have water at different tempera...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped from the top of a tower. In the last second of motio...
Text Solution
|
- Ratio of the wavelengths of first line of Lyman series and first line ...
Text Solution
|
- A rocket of mass M is launched vertically from the surface of the eart...
Text Solution
|
- The series combination of two batteries both of the same emf 10 V, bu...
Text Solution
|