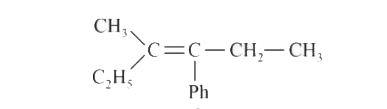
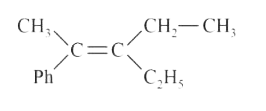
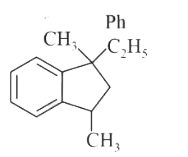
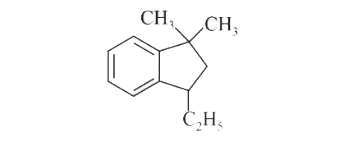
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-JEE MAIN REVISION TEST - 28-CHEMISTRY (SECTION-2)
- The major product of the following equation is. C(2)H(5)-overset(CH(...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following cell reaction. 2Fe(s)+O(2)(g)+4H^(+)(aq)rarr2...
Text Solution
|
- 10mL of 1mM surfactant solution forms a monolayer covering 0.24cm^(2) ...
Text Solution
|
- When the following aldohexose exists in its D-configuration, the total...
Text Solution
|
- For an element, Cp = 23 + 0.01 T("JK"^(-1)"mol"^(-1)) . If temperatur...
Text Solution
|
- The spin only magnetic moment value of Cr(CO)(6) is
Text Solution
|