A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GASEOUS STATE & THERMODYNAMICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE MAIN (ARCHIVE )|81 VideosGASEOUS STATE & THERMODYNAMICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE ADVANCED (ARCHIVE )|111 VideosGASEOUS STATE & THERMODYNAMICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise Level - 1|75 VideosENERGY & MOMENTUM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE ADVANCE (ARCHIVE) - TRUE/FALSE TYPE|1 VideosGRAVITATION
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advance (Archive) TRUE/FALSE|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-GASEOUS STATE & THERMODYNAMICS-Level - 2
- Experiment 1.When the two containers are weighed, @A = 225 g, W = 160 ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical containers joined by a small pipe initially contain the ...
Text Solution
|
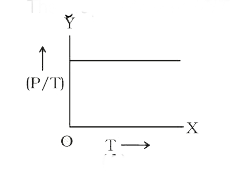
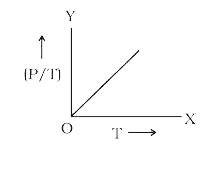
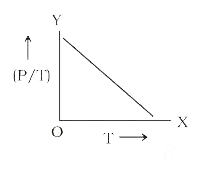
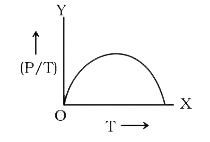
- The graph between (P/T) and T for a gas at constant volume will be:
Text Solution
|
- For a given thermodynamic process, the P – V diagram is as shown below...
Text Solution
|
- A partition divides a container having insulated walls into two compar...
Text Solution
|
- During an experiment, an ideal gas is found to obey a condition (p^2)/...
Text Solution
|
- During an experiment, an ideal gas is found to obey a condition Vp^2 =...
Text Solution
|
- Corresponding to isobaric process match the following two columns.
Text Solution
|
- Container A holds an ideal gas at a pressure 1 xx10^5 Pa and at 300 K...
Text Solution
|
- Container A holds an ideal gas at a pressure 1 xx10^5 Pa and at 300 K...
Text Solution
|
- Container A holds an ideal gas at a pressure 1 xx10^5 Pa and at 300 K...
Text Solution
|
- Two gases have the same initial pressure, volume and temperature. They...
Text Solution
|
- The volume of air increases by 10% in the adiabatic expansion. The app...
Text Solution
|
- Choose the correct option: In the arrangement shown in Fig. gas is t...
Text Solution
|
- Match the column I with column II.
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas is kept in two adjacent chambers of volume V and 2V, sepa...
Text Solution
|
- 3 mole of an ideal gas is taken through the process shown. BC is adiab...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas undergoes a process T = 300 + 2V. Then amount...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas whose adiabatic exponent is gamma = 4/3 unde...
Text Solution
|
- Find the amount of work done to increase the temperature of one mole j...
Text Solution
|