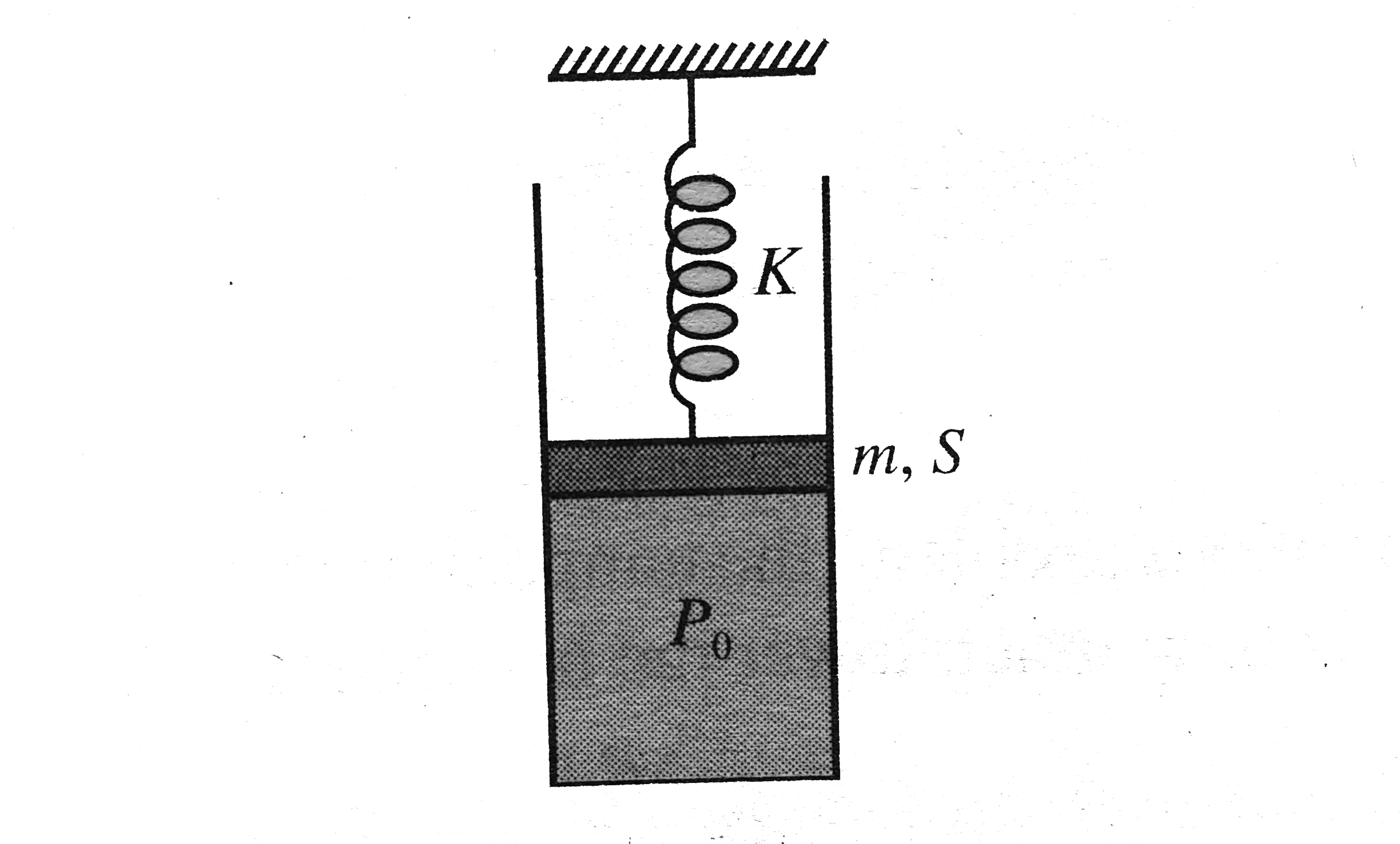
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GASEOUS STATE & THERMODYNAMICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE MAIN (ARCHIVE )|81 VideosGASEOUS STATE & THERMODYNAMICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE ADVANCED (ARCHIVE )|111 VideosGASEOUS STATE & THERMODYNAMICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise Level - 1|75 VideosENERGY & MOMENTUM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE ADVANCE (ARCHIVE) - TRUE/FALSE TYPE|1 VideosGRAVITATION
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advance (Archive) TRUE/FALSE|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-GASEOUS STATE & THERMODYNAMICS-Level - 2
- Two gases have the same initial pressure, volume and temperature. They...
Text Solution
|
- The volume of air increases by 10% in the adiabatic expansion. The app...
Text Solution
|
- Choose the correct option: In the arrangement shown in Fig. gas is t...
Text Solution
|
- Match the column I with column II.
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas is kept in two adjacent chambers of volume V and 2V, sepa...
Text Solution
|
- 3 mole of an ideal gas is taken through the process shown. BC is adiab...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas undergoes a process T = 300 + 2V. Then amount...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas whose adiabatic exponent is gamma = 4/3 unde...
Text Solution
|
- Find the amount of work done to increase the temperature of one mole j...
Text Solution
|
- A certain mass of an ideal gas is at pressure P(1) and volume V(1). If...
Text Solution
|
- Cp is always greater than Cv for a gas, which of the following stateme...
Text Solution
|
- A system undergoes a cyclic process in which it absorbs Q(1) heat and ...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas of mass m in a state A goes to another state B Vialpha th...
Text Solution
|
- Two mole of Hydrogen and three mole of Helium are mixed at room temper...
Text Solution
|
- For a gas, molar specific heat in a process is greater then CV . Which...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a monoatomic ideal gas undergoes the process ArarrB in the...
Text Solution
|
- Molar heat capacity of gas whose molar heat capacity at constant volum...
Text Solution
|
- A container of volume 4V(0) made of a perfectly non- conducting materi...
Text Solution
|
- A container of volume 4V(0) made of a perfectly non- conducting materi...
Text Solution
|
- A container of volume 4V(0) made of a perfectly non- conducting materi...
Text Solution
|