Law of Conservation of Mechanical Energy : The total mechanical energy of a system (E) is defined as the sum of the kinetic energy (K) and the potential energy (U) of the system, i.e., E = K + U
According to the law of conservation of mechanical energy:
The total mechanical energy of a system remains constant if the only force that does work is a conservative force.
Let us consider a body of mass m placed at A as shown in
h = AB = height of the body above the ground
x = distance of any point C from A
g = acceleration due to gravity at the place
`v_1` = velocity of the body at C
v = velocity of the body at B, a point just above the ground. The velocity at the point A is zero.
At the point A

Potential energy at A, i.e., `U_1 = mgh`
Kinetic energy at A, i.e., `K_1 = 0`
Total mechanical energy at A, i.e., `E_1 = mgh + 0 = mgh … (1)`
At the point C
As the body covers a distance x when it moves from A to C and `v_1` is the velocity at C, then from
`v^2 - v_0^2 = 2` we get : `v_1^2 = 0 = 2 gx` (As `v = v_1, v_0 = 0, a =g, s = x)` or `v_1^2 = 2 gx`
Kinetic energy at C, i.e., `" "K_2 = 1/2 mv_1^2 = 1/2 m xx 2 gx = mgx`
Potential energy at C, i.e., `" "U_2 = mg (h – x)`
Total mechanical energy at C, i.e., `" "E_2 = mgx + mg(h – x) = mgh …(2)`
At the point B
From `v_2 - v_0^2 = 2 as, v^2 -0 = 2gh ("as" v = v, v_0 = 0 , a = g, s = h)`
or, `v^2 = 2gh`
Kinetic energy at B, i.e., `" "K_3 = 1/2 mv^2 = 1/2 m xx 2 gh = mgh`
Potential energy at B, i.e., `U_3 = 0`
Total mechanical energy at B, i.e., `E_3 = mgh + 0 = mgh …(3)`
From eqns. (1), (2) and (3), `E_1 = E_2 = E_3`
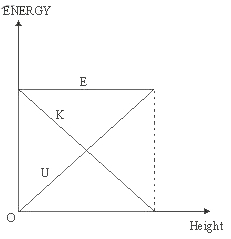
Clearly, total mechanical energy of the body at the points A, B and C (also at any other point) is the same. Thus, we find the total mechanical energy throughout the free fall is conserved. As the body falls down, the potential energy goes on decreasing whereas the kinetic energy goes on increasing. The variation of kinetic energy (K) and potential energy (U) and the constancy of the mechanical energy (E) have been represented graphically.
.

 .
.