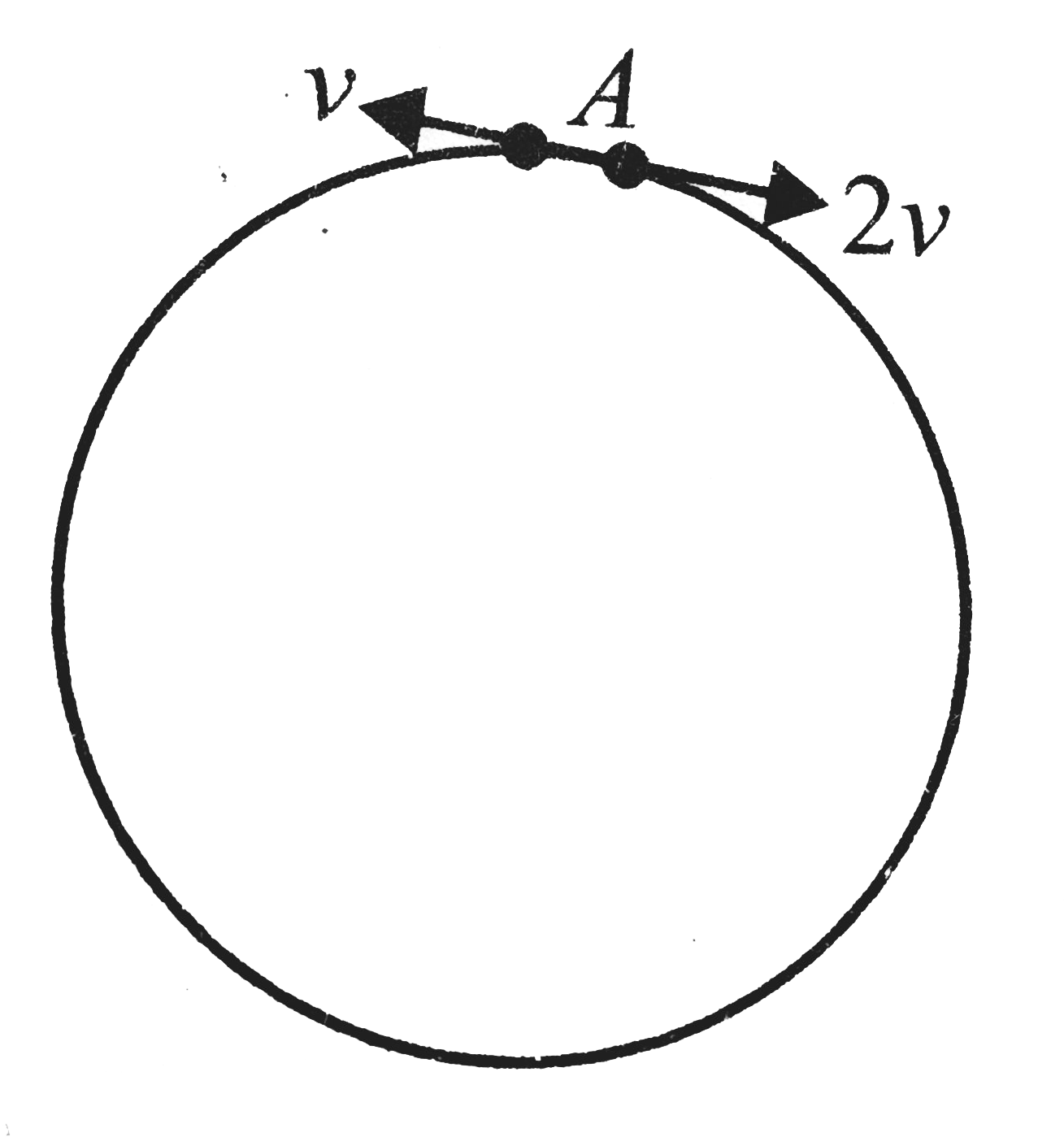
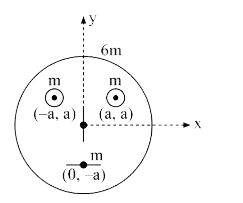
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ENERGY & MOMENTUM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE ADVANCE (ARCHIVE) - PARAGRAPH QUESTIONS|5 VideosENERGY & MOMENTUM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE ADVANCE (ARCHIVE) - ASSERTION & REASON TYPE|1 VideosENERGY & MOMENTUM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE MAIN (ARCHIVE)|53 VideosELECTROSTATICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advanced (Archive)|89 VideosGASEOUS STATE & THERMODYNAMICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE ADVANCED (ARCHIVE )|111 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-ENERGY & MOMENTUM-JEE ADVANCE (ARCHIVE)
- A block (B) is attached to two unstriched sprig S(1) and S(2) with spr...
Text Solution
|
- Look at the drawing given in the figure which has been drawn with ink ...
Text Solution
|
- Two small particles of equal masses start moving in opposite direction...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 2kg is free to move along the x-axis. It is at rest an...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 0.2 kg rests on a vertical post of height 5 m. A bullet...
Text Solution
|
- The work done an a particle of mass m by a force K[(x)/((x^(2) + y^(...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is projected from the ground with an initial spee...
Text Solution
|
- A tennis ball dropped on a horizontal smooth surface , it because back...
Text Solution
|
- A wire, which passes through the hole in a small bead, is bent in the ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider regular polygons with number of sides n = 3, 4, 5 ...... as s...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is alw...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and B. each of mass m, are connected by a massless spring...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls having linear momenta vecp(1)=phati and vecp(2)=-phati, und...
Text Solution
|
- A point mass of 1 kg collides elastically with a stationary point mass...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass M has a circular cut with a frictionless surface as sh...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is initially at rest at the origin. It is subject...
Text Solution
|
- A small particle of mass m moving inside a heavy, hollow and straight ...
Text Solution
|
- Statement I: In an elastic collision between two bodies, the relative ...
Text Solution
|
- A 20 g bullet pierces through a plate of mass M(1) = 1 kg and then com...
Text Solution
|
- A circular plate of uniform thickness has a diameter of 28 cm. A circu...
Text Solution
|