Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
LIQUIDS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL -1|90 VideosLIQUIDS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL -2|50 VideosLIQUIDS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL-0 ( Short Answer Type - I )|7 VideosLAWS OF MOTION
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise IMPECCABLE|53 VideosMAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advanced (Archive)|78 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-LIQUIDS-LEVEL-0 ( Short Answer Type - II )
- Define Surface tension. Write its formula. What is its S.I unit?
Text Solution
|
- State Bernoulli’s Principle. A man standing while on a railway platfor...
Text Solution
|
- A liquid drop of diameter D breaks up into 27 drops. Find the resultan...
Text Solution
|
- Define Stoke’s law. Define and derive an expression for terminal veloc...
Text Solution
|
- Molarity of pure water is
Text Solution
|
- The equation of continuity leads to
Text Solution
|
- Define coeffiecient of viscosity of a liquid. Write down its dimension...
Text Solution
|
- In a test experiment of a model aeroplane in a wind tunnel, the flow s...
Text Solution
|
- A planet travels in an elliptical orbit about a star as shown. At what...
Text Solution
|
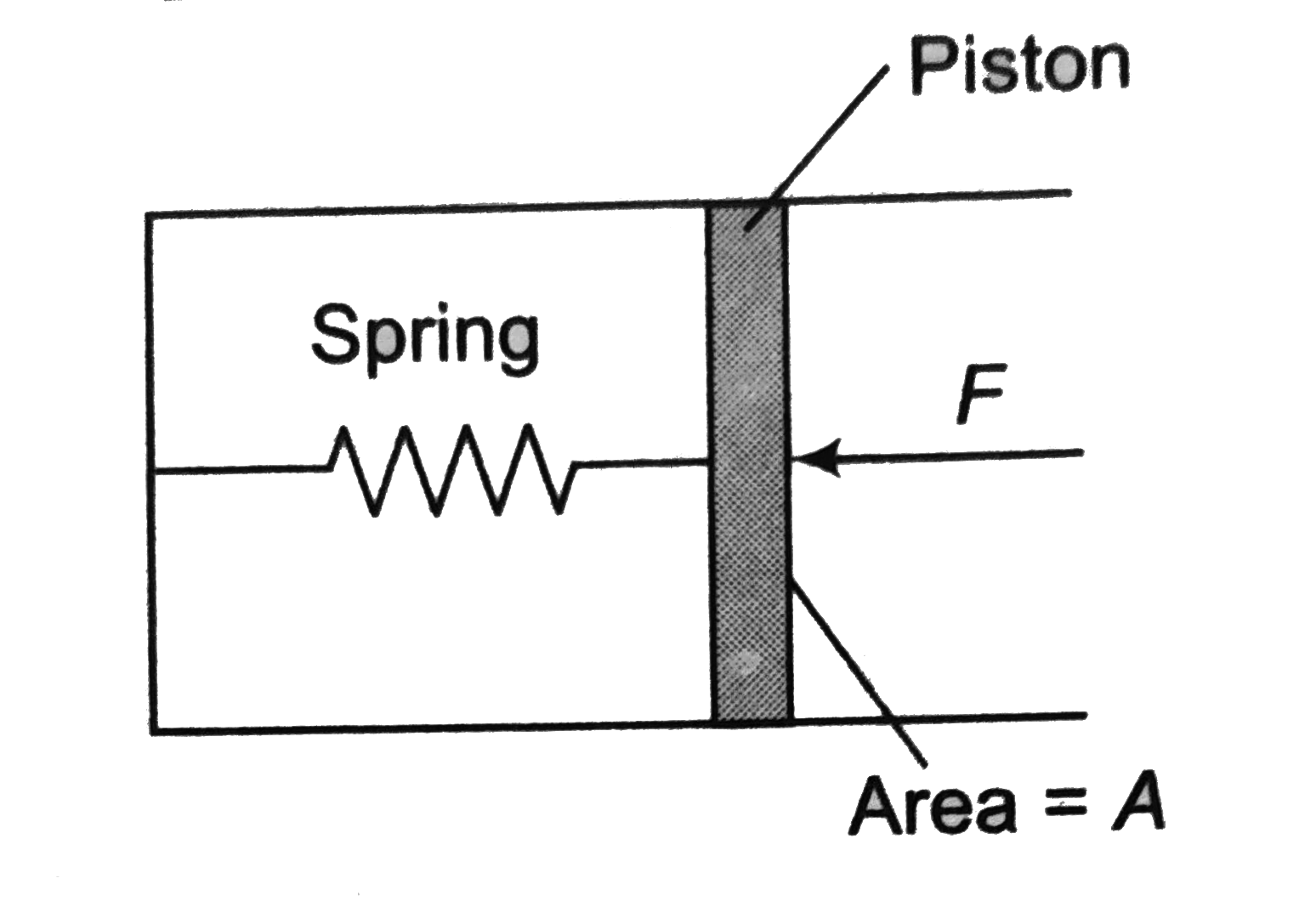
- The pressure gauge shown in figure has a spring for which k=60N//m and...
Text Solution
|
- What is the excess pressure inside a bubble of soap solution of radius...
Text Solution
|
- Bunty was fond of painting. He observed that hairs of paint brush do n...
Text Solution
|
- What is capillarity? Derive an expression for the height to which the ...
Text Solution
|
- State and prove Bernouli's theorem.
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical tank whose cross-section area is 2000 cm^2 has a hole ...
Text Solution
|