The stress strain graph for a metal wire is shown in the fig. Up to the point E, the wire returns to its original state O along the curve EPO, when it is gradually unloaded. Point B corresponds to the fracture of the wire.
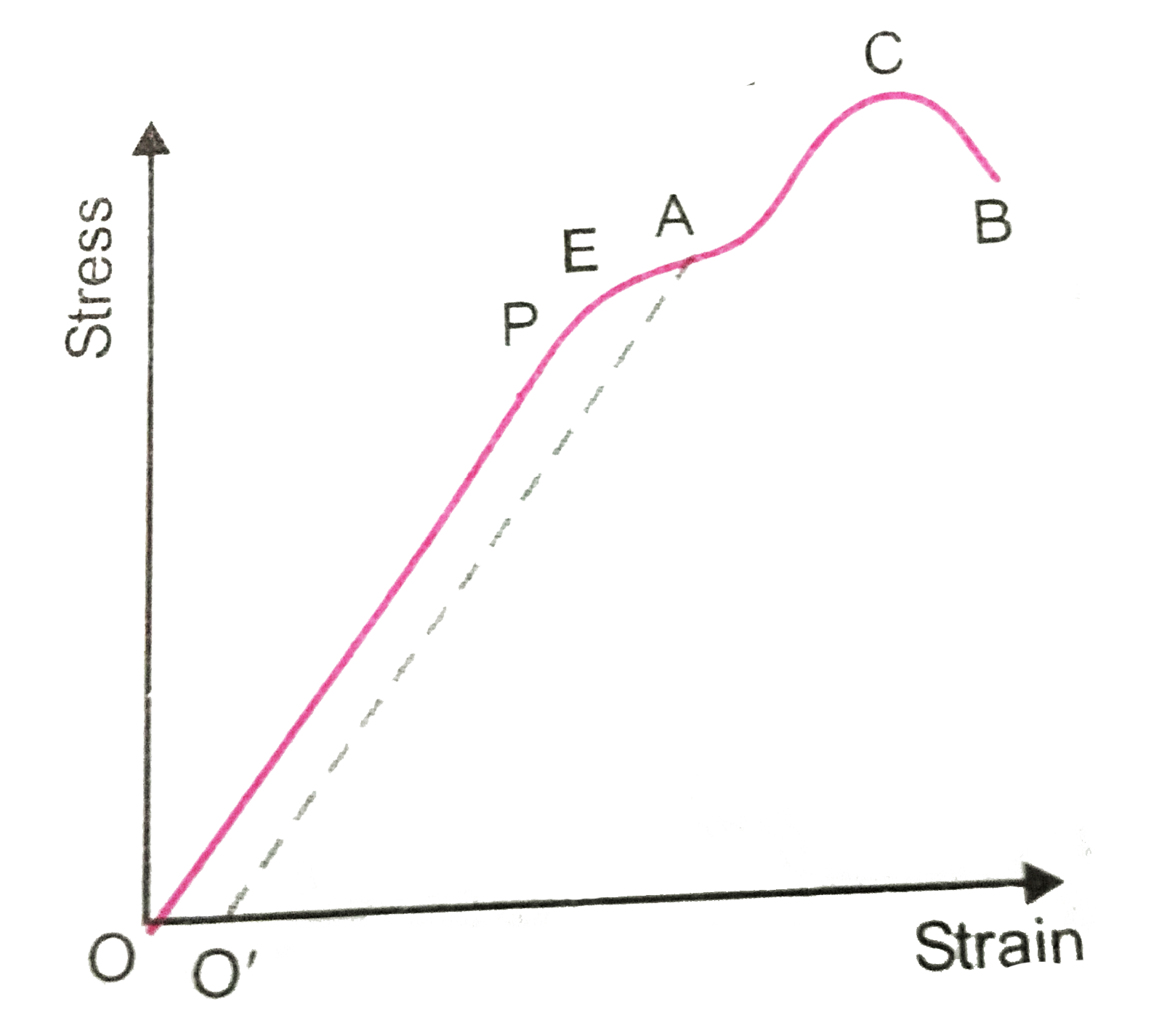
(a) Up to what point on the curve is Hooke's law obeyed? (this point some times called proportional limits).
(b) Which point on the curve corresponding to elastic limit or yield point of the wire?
(c ) Indicate the elastic and plastic regions of the stress-strain graph.
(d) Describe what happens when the wire is loaded up to a stress corresponding to the point A on the graph and then unloaded gradually. In particular explain the dotted curve.
(e) What is peculiar about the portion of the stress- strain graph from C to B? Up to what stress can the wire be subjected without causing fracture?