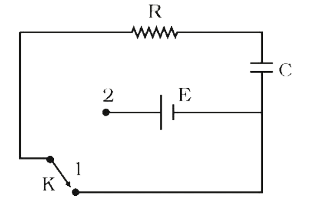
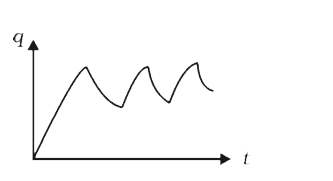
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CAPACITORS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Main (Archive) LEVEL-1|36 VideosCAPACITORS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advance ( Archive ) LEVEL 2|1 VideosCAPACITORS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL 1 (MCQs)|60 VideosBASIC MATHEMATICS & VECTORS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise Impeccable|50 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise IN-CHAPTER EXERCISE-F|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-CAPACITORS-LEVEL 2
- A capacitor C(1) =1.0 muF is charged up to a voltage V=60 V by connec...
Text Solution
|
- Two capacitors of 2muF and 3muF are charged to 150 V and 120 V, respec...
Text Solution
|
- In the shown circuit involving a resistance Romega, capacitor of capac...
Text Solution
|
- In the shown circuit involving a resistance Romega, capacitor of capac...
Text Solution
|
- In each situation of column-I, a circuit involving two non-ideal cell...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical capacitors C(1),C(2) and C(3) have a capacitance of 1...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel capacitors of capacitances C and 2C are connected in para...
Text Solution
|
- When a dielectric slab is inserted between the plates of one of the tw...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a disconnected plate capacitor of capacity 10 muF with air fi...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel pate capacitor of capacitance ‘C’ has charge on its plates ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical capacitors are connected in series, and the combination ...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitor having a capacitance of 100muF is charged to a potential d...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitor having a capacitance of 100muF is charged to a potential d...
Text Solution
|
- Space between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor is filled with ...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel plate capacitor of area A and separation d is charged to po...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitor of capacitance C(1) is charged to a potential difference V...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitor C(1) is charged to a potential V and connected as shown wi...
Text Solution
|
- Two capacitors, C(1) and C(2), charged to a potential V/2 and V respec...
Text Solution
|
- An uncharged capacitor of capacitance is connected in a circuit with t...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown, all capacitors are initially uncharged. The capa...
Text Solution
|