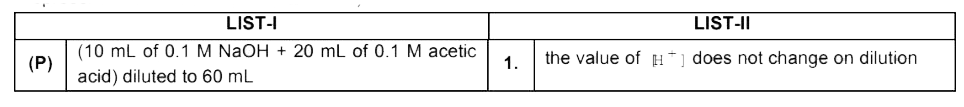
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
IONIC EQUILIBRIUM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise Illustration - 1|1 VideosIONIC EQUILIBRIUM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise Illustration - 2|1 VideosIONIC EQUILIBRIUM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE MAIN ( ARCHIVE )|50 VideosINTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE ADVANCED ARCHIVE|81 VideosJEE MAIN - 5
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise PART II : CHEMISTRY (SECTION - 2)|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-IONIC EQUILIBRIUM-JEE ADVANCED( ARCHIVE )
- For the reaction Ag(CN)(2)^(ɵ)hArr Ag^(o+)+2CN^(ɵ), the K(c ) at 25^...
Text Solution
|
- The average concentration of SO(2) in the atmosphere over a city on a ...
Text Solution
|
- For a sparingly soluble salt ApBq, the relationship of its solubility...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the correct order of solubility of Na(2)S,CuS and ZnS in aque...
Text Solution
|
- A solution containing Mn^(2+),Fe^(2+),Zn^(2+)andHg^(2+) with a molar c...
Text Solution
|
- 0.1 M of HA is titrated with 0.1 M NaOH, calculate the pH at end point...
Text Solution
|
- HX is a weak acid (K(a) = 10^(-5)). If forms a salt NaX(0.1M) on react...
Text Solution
|
- CH(3)NH(2)(0.1"mole",K(b)=5xx10^(-4)) is added to 0.08 moles of HCI a...
Text Solution
|
- The solubility product constant (K(sp)) of salts of types MX, MX(2), a...
Text Solution
|
- The dissociation constant of a substitued benzoic acid at 25^(@)C is 1...
Text Solution
|
- Amongst the following, the total number of compounds whose aqueous sol...
Text Solution
|
- Aqueous solution of HNO(3),CH(3),CH(3)COOH, and CH(3)COOK of identical...
Text Solution
|
- The total number of diprotic acids among the following is H(3)PO(4),...
Text Solution
|
- In 1L saturated solution of AgCl[K(SP)(AgCl)= 1.6xx10^(-10)], 0.1 mole...
Text Solution
|
- (A)Find the solubility product of a saturated solution of Ag(2)CrO(4) ...
Text Solution
|
- If K(sp) of Ag(2)CO(3) is 8xx10^(-12) the molar solubility of Ag(2)CO(...
Text Solution
|
- When 100mL of 1.0M HCl was mixed with 100 mL of 1.0 M NaOH in an insul...
Text Solution
|
- When 100mL of 1.0M HCl was mixed with 100 mL of 1.0 M NaOH in an insul...
Text Solution
|
- The solubility of a salt of weak acid (AB) at pH 3 is Y xx 10^(-3) "...
Text Solution
|
- Dilution processes of different aqueous solutions, with water, are giv...
Text Solution
|