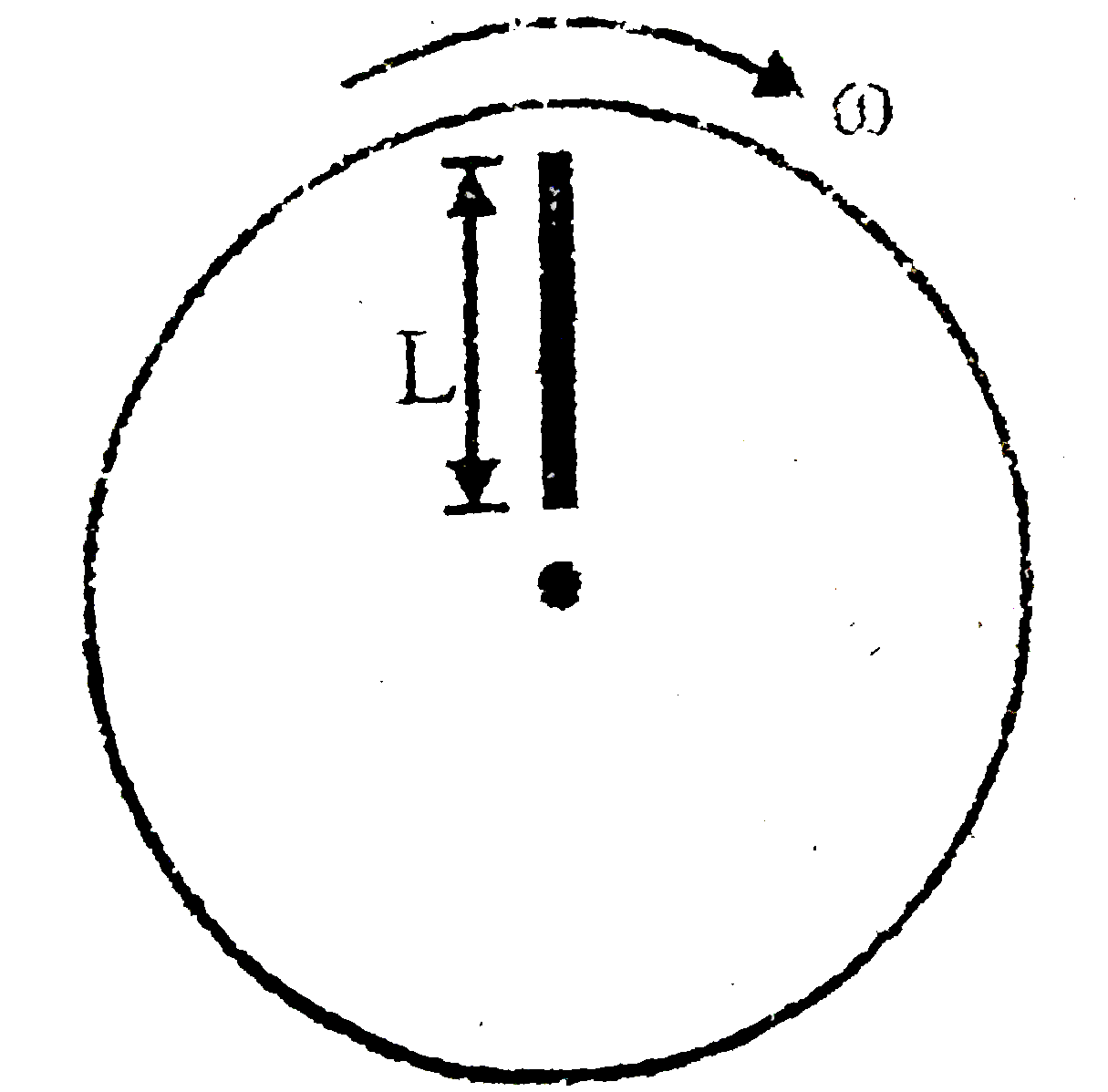
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ROTATIONAL MOTION
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL - 2 (Angular Momentum, Collision)|20 VideosROTATIONAL MOTION
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE MAIN (ARCHIVE)|58 VideosROTATIONAL MOTION
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL - 2 (Torque, Fixed and Rotation)|10 VideosREVISION TEST-2 JEE
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise PHYSICS|25 VideosSIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise 7-previous year question|46 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-ROTATIONAL MOTION -LEVEL - 2 (General rigid body motion, Rolling)
- A disc of radius R is rolling purely on a flat horizontal surface, wit...
Text Solution
|
- A system of uniform cylinders and plates is shown in the figure. All ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of mass m and length L lies radialy on a disc rotating w...
Text Solution
|
- A yo-yo is placed on a rough horizontal surface -and a constant force ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere of mass M and radius R is pulled horizontally on a roug...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of circumference s is at rest at a point A on horizontal surfac...
Text Solution
|
- A stepped cylinder having mass 50 kg and a radius of gyration (K) of 0...
Text Solution
|
- A small sphere of mass 1 kg is rolling without slipping with linear sp...
Text Solution
|
- A small sphere of mass 1 kg is rolling without slipping with linear sp...
Text Solution
|
Text Solution
|