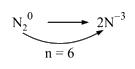
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
STOICHIOMETRY-II
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL (2)|65 VideosSTOICHIOMETRY-II
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Main (Archive)|21 VideosSTOICHIOMETRY-II
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advanced (Archive)|43 VideosSTOICHIOMETRY - I
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advanced (Archive)|31 VideosSTRUCTURE OF ATOM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise IN-CHAPTER EXERCISE-F|7 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-STOICHIOMETRY-II-LEVEL (1)
- One gas bleaches the colour of flowers by reduction while the other by...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following changes requires a reducing agent ?
Text Solution
|
- N(2) + 3H(2) to 2NH(3) In this reaction, equivalent weight of N(2) is...
Text Solution
|
- NaHC(2)O(4) is neutralised by NaOH. It can also be oxidised by KMnO(4...
Text Solution
|
- Cl(2) changes to Cl^(-) in cold NaOH. The equivalent weight of Cl(2)...
Text Solution
|
- Equivalent weights of KMnO(4) in acidic medium, alkaline medium and n...
Text Solution
|
- 1 mole of ferric oxalate is oxidised by x mole of MnO(4)^(-) in acidic...
Text Solution
|
- Which has maximum number of equivalent per mole of the oxidant?
Text Solution
|
- NH(3) is oxidised to NO by O(2) (air) in basic medium. Number of equ...
Text Solution
|
- In the following unbalanced redox reaction, Cu(3)P+Cr(2)O(7)^(2-) ra...
Text Solution
|
- NaHC(2)O(4) is 0.1 M when neutralised with NaOH. Hence, it is ...... w...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is not oxidised by MnO(2) ?
Text Solution
|
- 100 mL of NaHC(2)O(4) required 50 mL of 0.1M KMnO(4) solution in acid...
Text Solution
|
- In a titration, H(2)O(2) is oxidised to O(2) by MnO(4)^(-). 24 mL of...
Text Solution
|
- What is Thiol?
Text Solution
|
- I^(-) reduces HNO(2) to :
Text Solution
|
- KMnO(4) oxidises I^(-) to I(2) in acidic medium. The equivalent wei...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction 3Br(2)+6OH^(ө)-lt5Br^(ө)+BrO(3)^(ө)+3H(2)O Equiva...
Text Solution
|
- Moles of KHC(2)O(4) (potassium acid oxalate) required to reduce 100ml...
Text Solution
|
- Number of electron involved in the reduction of Cr(2)O(7)^(2-) ion in ...
Text Solution
|