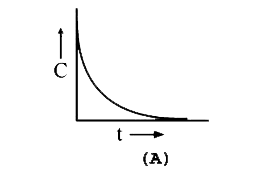
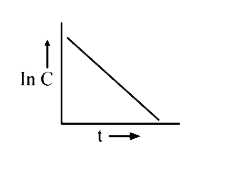
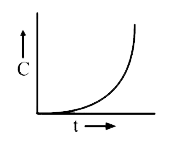
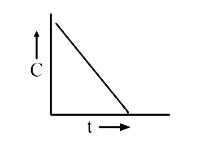
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL KINETICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise Level-2 ( Numerical Value Type for JEE Main )|15 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Main (Archive)|56 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise Level-1|75 VideosCHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise IN-CHAPTER EXERCISE - G|10 VideosCHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise IN - CHAPTER EXERCISE - L|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-CHEMICAL KINETICS -Level-2
- The half-life period of a first-order chemical reaction is 6.93 min. T...
Text Solution
|
- The unit of rate constant for a second order reaction is
Text Solution
|
- The plote between concentration versus time for a zero order reaction ...
Text Solution
|
- Under the same reaction conditions, the intial concentration of 1.386 ...
Text Solution
|
- For a reaction, A+2B to C, rate is given by +(d[C])/(dt)=k[A][B], henc...
Text Solution
|
- Which represents first order reaction out of I, II and III?
Text Solution
|
- For a 1^(st) order decomposition, overall k will be given by :
Text Solution
|
- For a first order reaction with rate constant 'k' and initial concentr...
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant of a first order reaction is 6.9xx10^(-3)s^(-1). How...
Text Solution
|
- For the homogeneous elementary reaction, A+B rarrC, the unit of rate ...
Text Solution
|
- How much time is requred for two - third completion of a first order r...
Text Solution
|
- A first orde reaction is 75% completed after 32min. When was 50% of th...
Text Solution
|
- In the reaction 2N(2)O(5) rarr 4NO(2) + O(2), initial pressure is 500...
Text Solution
|
- The activation energy of exothermic reaction ArarrB is 80 kJ "mol"^(-1...
Text Solution
|
- For a gaseous reaction, following data is given: ArarrB, k(1)= 10^(1...
Text Solution
|
- Given the following diagram for the reaction A+B rarr C+D The enthalpy...
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant of a first order reaction at 27^@C is 10–3 min–1. Th...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction 2NH(3) to N(2) + 3H(2), If - (d[NH(3)])/(dt) = k(!)...
Text Solution
|
- A catalyst lowers the enrgy of activation by 25%, temperature at which...
Text Solution
|
- In the following graphical representation for the reaction A rarr B, t...
Text Solution
|