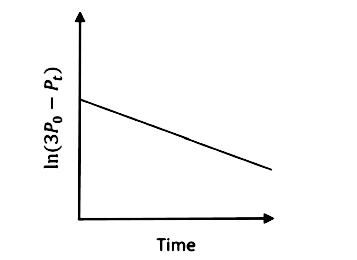
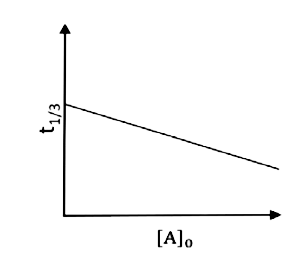
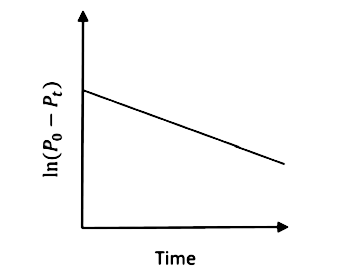
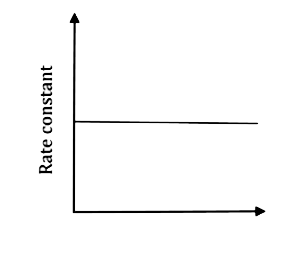
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-CHEMICAL KINETICS -JEE Advanced (Archive)
- For the given reaction, A + B rarr Products Following data are given ...
Text Solution
|
- 2X(g) rarr 3Y(g)+2Z(g) {:("Time (in min)",0,100,200,):} |{:("Parti...
Text Solution
|
- Ag^(+) + NH(3) ltimplies [Ag(NH(3))]^(+), k(1)=6.8 xx 10^(-5) [Ag(NH...
Text Solution
|
- Conisder a reaction aG+bH rarr Products. When concentration of both th...
Text Solution
|
- Under the same reaction conditions, the intial concentration of 1.386 ...
Text Solution
|
- For a first order reaction A rarr P, the temperature (T) dependent rat...
Text Solution
|
- The concentration of R in the reaction R rarr P was measured as a func...
Text Solution
|
- For the first order reaction 2N(2)O(5)(g) rarr 4NO(2)(g) + O(2)(g)
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound undergoes first decompoistion. The time taken for ...
Text Solution
|
- In the reaction, P+Q rarr R+S the time taken for 75% reaction of P i...
Text Solution
|
- For the elementary reaction MrarrN, the rate of disappearance of M inc...
Text Solution
|
- A closed vessel with rigid walls contains 1 mole of .(92)^(238)U and 1...
Text Solution
|
- According to the Arrhenius equation,
Text Solution
|
- A plot of the number of neutrons (n) against the number of protons (p...
Text Solution
|
- In a bimolecular reaction, the steric factor P was experimentally dete...
Text Solution
|
- For a first order reaction A(g)rarr2B(g)+C(g) at constant volume and 3...
Text Solution
|
- For a first order reaction A(g) rarr 2B(g) + C(g) at constant volume a...
Text Solution
|
- In the decay sequence, {:(238),(92):}Uoverset(-x(1))rarr{:(234),(90)...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the kinetic data given in the following table for the reactio...
Text Solution
|
- The decomposition reaction 2N(2)O(5) (g) rarr 2N(2) O(4) (g) +O(2) (g)...
Text Solution
|