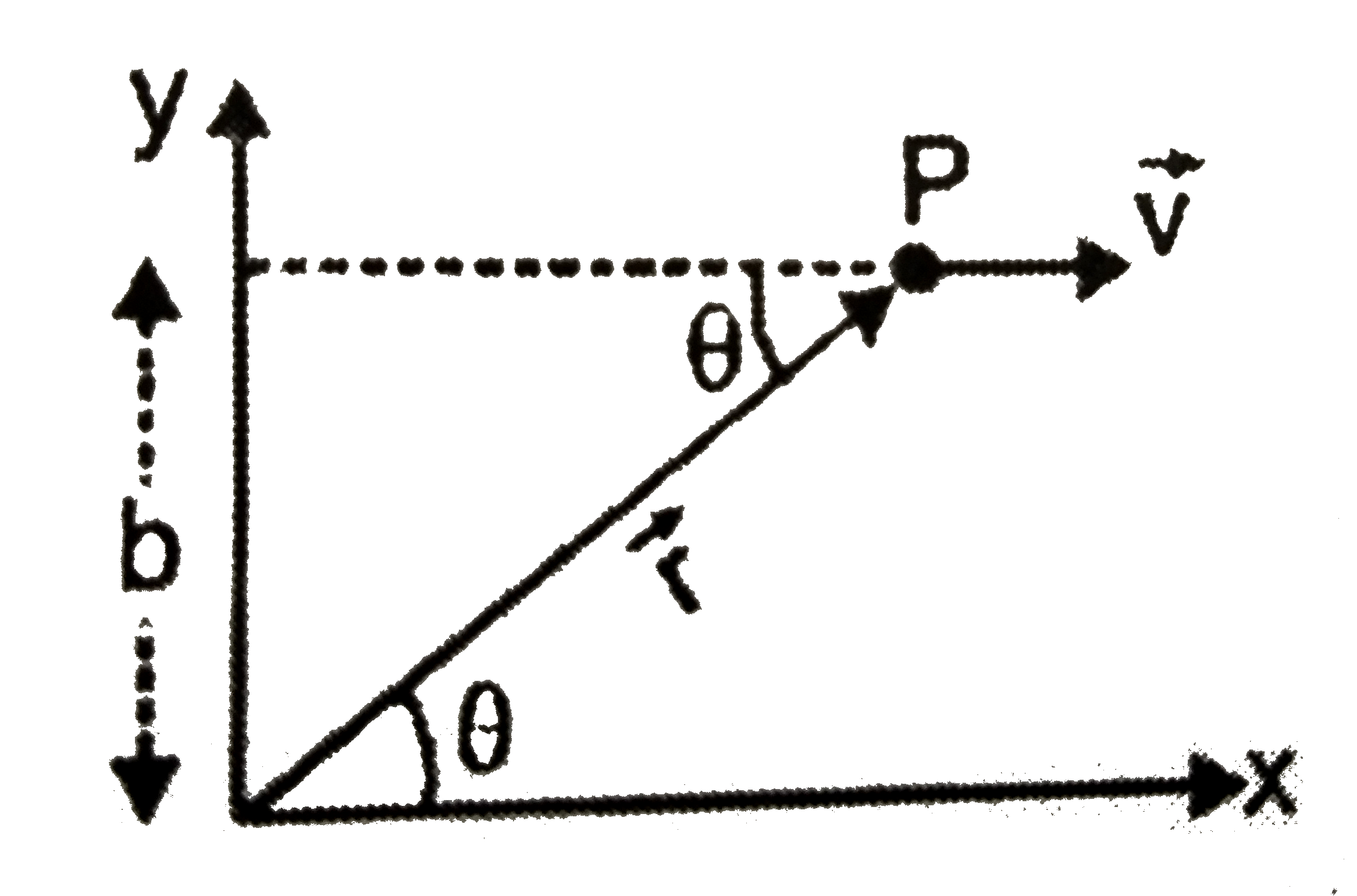
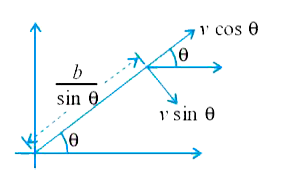
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Motion in Straight Line
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise SOLVED EXAMPLES|20 VideosMotion in Straight Line
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise PRACTICE EXERCISE|80 VideosMOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE & PLANE
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise IMPECCABLE|52 VideosMotion in Two Dimensions
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise MCQ|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-Motion in Straight Line -IN-CHAPTER EXERCISE-J
- A particle moving parallel to x-axis as shown in fig. such that at all...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is alw...
Text Solution
|
- If the equation for the displacement of a particle moving in a circula...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves in a circular path with a uniform speed. Its motion i...
Text Solution
|
- If the speed and radius both are trippled for a body moving on a circu...
Text Solution
|
- When a body moves with a constant speed along a circle
Text Solution
|
- A string of length 0.1 m cannot bear a tension more than 100 N. It is ...
Text Solution
|
- The radius of the circular path of a particle is doubled but its frecu...
Text Solution
|
- A 0.5 kg ball moves in a circle of radius 0.4 m at a velocity of 4 m/s...
Text Solution
|
- A body is revolving with a constant speed along a circle. If its direc...
Text Solution
|
- Let a(f) and a(t) represent radial and tangential accelerations. The m...
Text Solution
|