Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-CURRENT ELECTRICITY-IN-CHAPTER EXERCISE-F
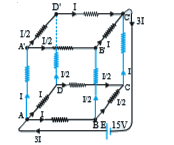
- A battery of 15 V and negligible internal resistance is connected acro...
Text Solution
|
- Three bulbs of 40 W , 60 W , 100 W are arranged in series with 220 vol...
Text Solution
|
- Two electric bulbs A and B are rated as 60 W and 100 W . They are conn...
Text Solution
|
- An electric immersion heator of 1.08 k W is immersed in water. After t...
Text Solution
|
- If two identical heaters each rated as (1000 W, 220V) are connecte...
Text Solution
|
- A heater boils certain amount of water in 15 minutes. Another heater b...
Text Solution
|
- For driving current of 2 A for 6 minute in a circuit 1000 J of work is...
Text Solution
|
- An electric bulb, marked 40 W and 200 V, is used in a circuit of suppl...
Text Solution
|
- Three equal resistors connected in series across a source of EMF...
Text Solution
|
- A 30V, 40 w lamp is to be operated on a 120 V DC lines. For proper glo...
Text Solution
|
- Two bulbs 60 W and 100 W designed for voltage 220 V are connected in s...
Text Solution
|