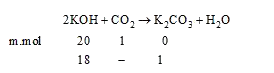A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-MOCK TEST 5-CHEMISTRY (SECTION 2)
- A bottle, which contains 200 ml of 0.1 M KOH, absorbs 1 millimole of C...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the heat of formation of methane in kcalmol^(-1) using the ...
Text Solution
|
- The number of atoms in one molecule of Epsom salt is
Text Solution
|
- The coagulation of 10 ml of colloidal solution of gold is completely p...
Text Solution
|
- The number of Pi bonds in one molecule of “Aspartame” is
Text Solution
|
- A buffer solution is prepared by mixing 10ml of 1.0 M acetic acid an...
Text Solution
|