A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH-STRAIGHT LINES-Chapter Test
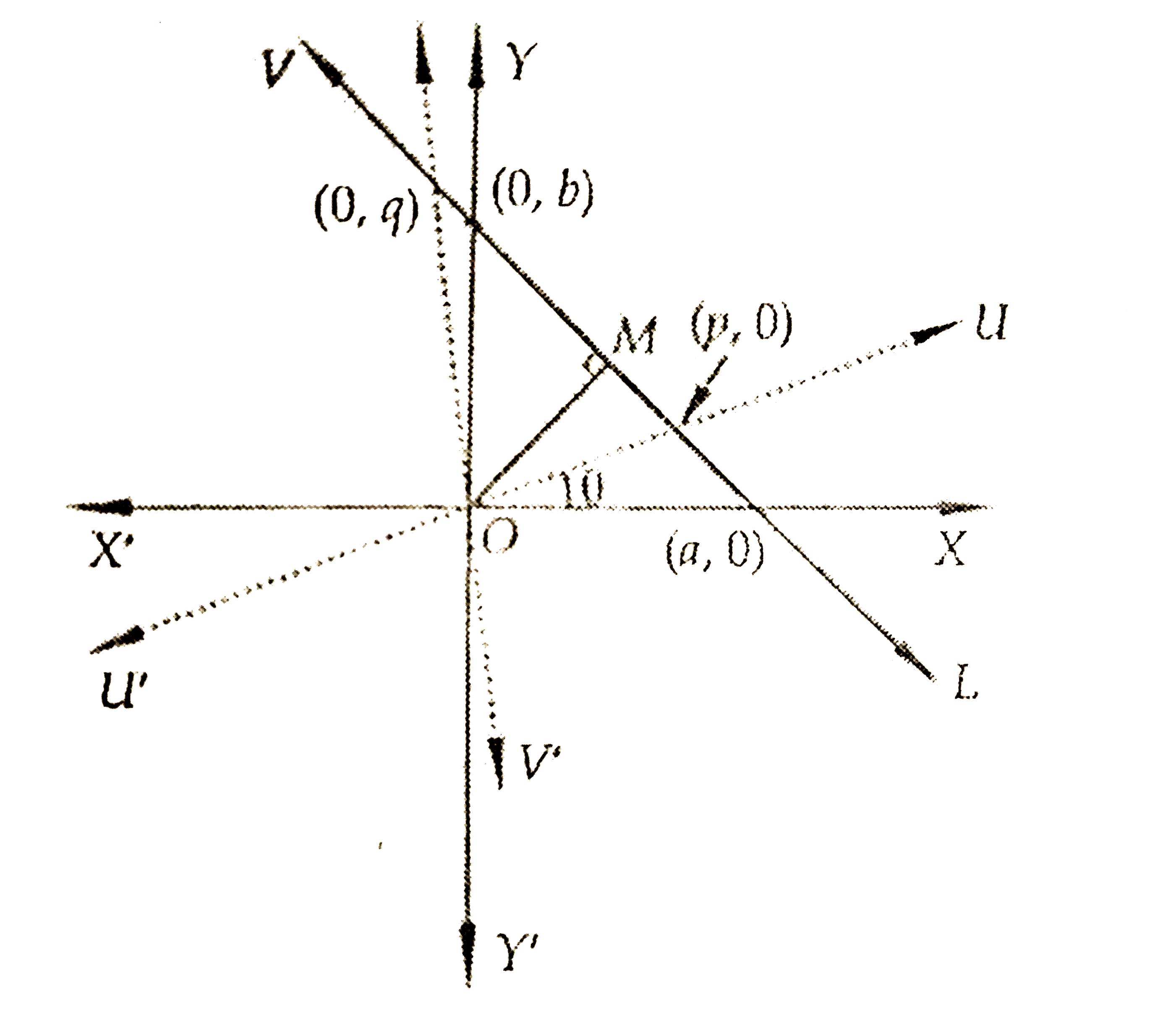
- Line L has intercepts aa n db on the coordinate axes. When the axes ar...
Text Solution
|
- The equation to a pair of opposite sides of a parallelogram are x^2-5x...
Text Solution
|
- The distance between the parallel lnes y=2x+4 and 6x-3y-5 is (A) 1 (B)...
Text Solution
|
- P is a point on either of the two lines y - sqrt(3)|x| = 2 at a dista...
Text Solution
|
- If one diagonal of a square is along the line x=2y and one of its vert...
Text Solution
|
- The line which is parallel to x-axis and crosses the curve y=sqrt(x) a...
Text Solution
|
- P(3,1),Q(6,5) and R(x,y) are three points such that PRQ is a right ang...
Text Solution
|
- Find the equation of the straight line which passes through the point ...
Text Solution
|
- What is the equation of the straight line which is perpendicular to y=...
Text Solution
|
- Find the perpendicular distance between the lines 3x+4y+9=0 and to 6x...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of the line passing through the point (1,2) and perpendic...
Text Solution
|
- The straight lines x+y=0, 3x+y-4=0 and x+3y-4=0 form a triangle which ...
Text Solution
|
- Triangle formed by x^(2)-3y^(2)=0 and x=4 is
Text Solution
|
- The co-ordinates of the orthocentre of the triangle bounded by the lin...
Text Solution
|
- the lines (p+2q)x+(p-3q)y=p-q for different values of p&q passes troug...
Text Solution
|
- Write the distance between the lines 4x+3y-11=0\ a n d\ 8x+6y-15=0.
Text Solution
|
- If the diagonals of a parallelogram ABCD are along the lines x+5y=7 a...
Text Solution
|
- The straight lines x+y-4=0, 3x+y-4=0 and x+3y-4=0 form a triangle, whi...
Text Solution
|
- Write the coordinates of the orthocentre of the triangle formed by ...
Text Solution
|
- A point equidistant from the line 4x + 3y + 10 = 0, 5x-12y + 26 = 0 an...
Text Solution
|
- The number of values of a for which the lines 2x+y-1=0 , a x+3y-3=0, a...
Text Solution
|