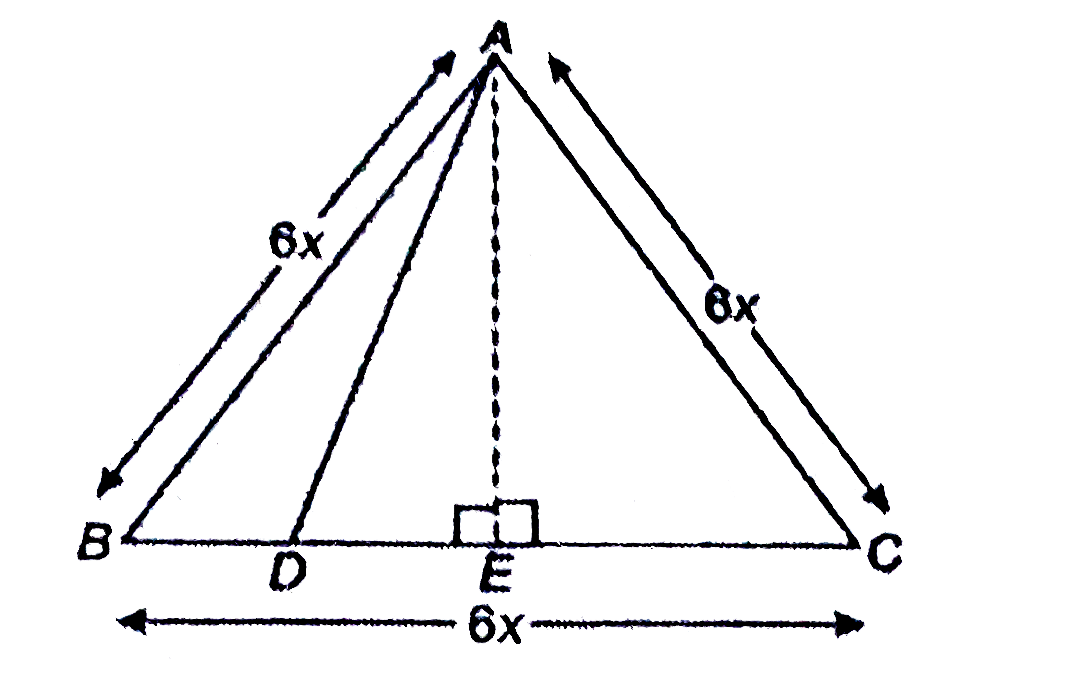
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
TRIANGLES
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise Problems From NCERT/ Exemplar|14 VideosTRIANGLES
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 6a|24 VideosSTATISTICS
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise Revision Exercise Long Answer Questions|4 VideosVOLUME AND SURFACE AREA OF SOLIDS
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise Revisions Exercise Long Answer Questions|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems