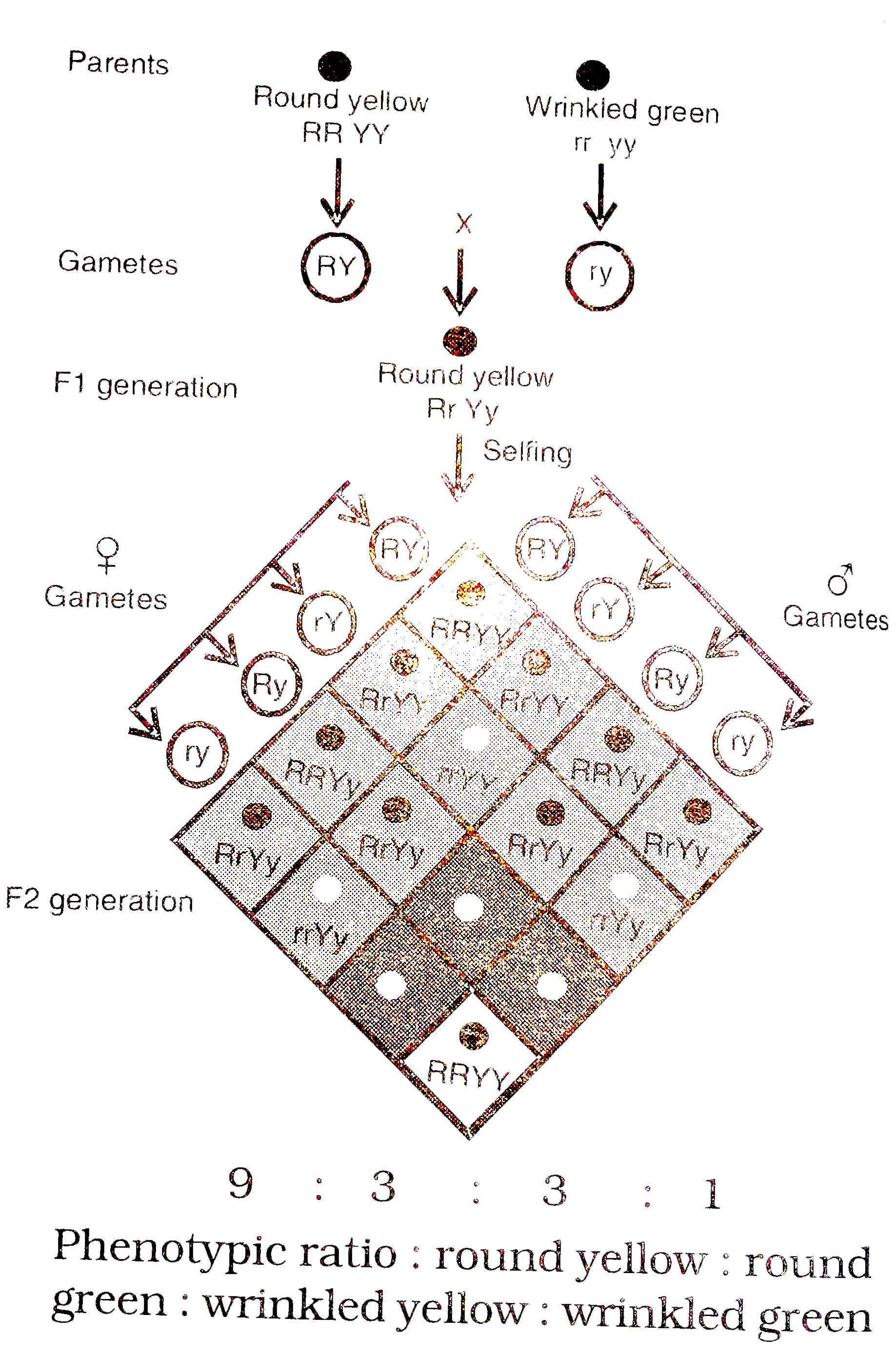
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
TRUEMAN BIOLOGY-GENETICS AND EVOLUTION -SECTION-D
- Define transcription. Where does transcription in eukaryotes takes pla...
Text Solution
|
- Define: Evolution Gene pool
Text Solution
|
- Two blood samples A and B picked up from the crime scene were handed o...
Text Solution
|
- Name the scientist who proved DNA as a hereditary material.
Text Solution
|
- With the help of one example each provide genetic explanation for the ...
Text Solution
|
- Name any two chromosomal disorders.
Text Solution
|
- Name any two mendelian disorder.
Text Solution
|
- Define Fossil. Mention its types.
Text Solution
|
- (a) State the central dogma in molecular biology. Who proposed it? Is ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Write what DNA replication refers to. (b ) List any three enzym...
Text Solution
|
- Explain inheritance of flower colour in Mirabilis jalapa. Mention the ...
Text Solution
|
- A child suffering from Thalassemia is born to a normal couple. But the...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the mechanism of sex-determination in humans. b) Differentia...
Text Solution
|
- Explain Mendel's law of independent assortment by taking a suitable ex...
Text Solution
|
- Name the species evolved post Industrialization in England.
Text Solution
|
- Who discovered mutation? Mention any two types.
Text Solution
|
- Fitness is the end result of the ability to adapt and get selected by ...
Text Solution
|
- The rate of appearance of new forms is linked to the life span of an o...
Text Solution
|
- Define isolation. Mention its types.
Text Solution
|
- To which phylum does Trilobite belongs to? Name the period they evolve...
Text Solution
|