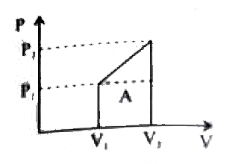
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PHYSICS WALLAH-THERMODYNAMICS-NEET Past 5 Years Questions
- The efficiency of carnot engine depends on
Text Solution
|
- PV Diagram for ideal gas in piston cylinder assembly undergoing a ther...
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following processes, heat is neither absorbed nor rel...
Text Solution
|
- The volume (V) of a monatomic gas varies with its temperature (T) as s...
Text Solution
|
- The efficiency of an ideal heat engine working between the freezing po...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of 0.1 g of water of 100^(@)C and normal pressure (1.013 xx 1...
Text Solution
|
- Thermodynamic process are indicated in the following diagram: Match...
Text Solution
|
- A Carnot engine, having an efficiency of eta= 1/10 as heat engine, is ...
Text Solution
|
- The volume of one mode of an ideal gas with adiabatic exponent gamma i...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a gas obeying the expantions P(V-b)=RT is made to expand f...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature inside a refrigerator is t2 °C and the room temperatur...
Text Solution
|
- A body cools from a temperature 3 T to 2 T in 10 minutes. The room tem...
Text Solution
|
- A gas is compressed isothermally to half its initial volume. The same ...
Text Solution
|
- A refrigerator works between 4^(@)C and 30^(@)C. It is required to rem...
Text Solution
|