A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CENTRE OF MASS
ALLEN |Exercise EXERCISE-III|41 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
ALLEN |Exercise EXERCISE-IV A|32 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
ALLEN |Exercise EXERCISE-I|40 VideosBASIC MATHEMATICS USED IN PHYSICS &VECTORS
ALLEN |Exercise EXERCISE-IV ASSERTION & REASON|11 VideosELASTICITY, SURFACE TENSION AND FLUID MECHANICS
ALLEN |Exercise Exercise 5 B (Integer Type Questions)|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN -CENTRE OF MASS-EXERCISE-II
- A bead of mass m and diameter d is sliding back and forth with velocit...
Text Solution
|
- A set of n identical cubical blocks lies at rest parallel to each othe...
Text Solution
|
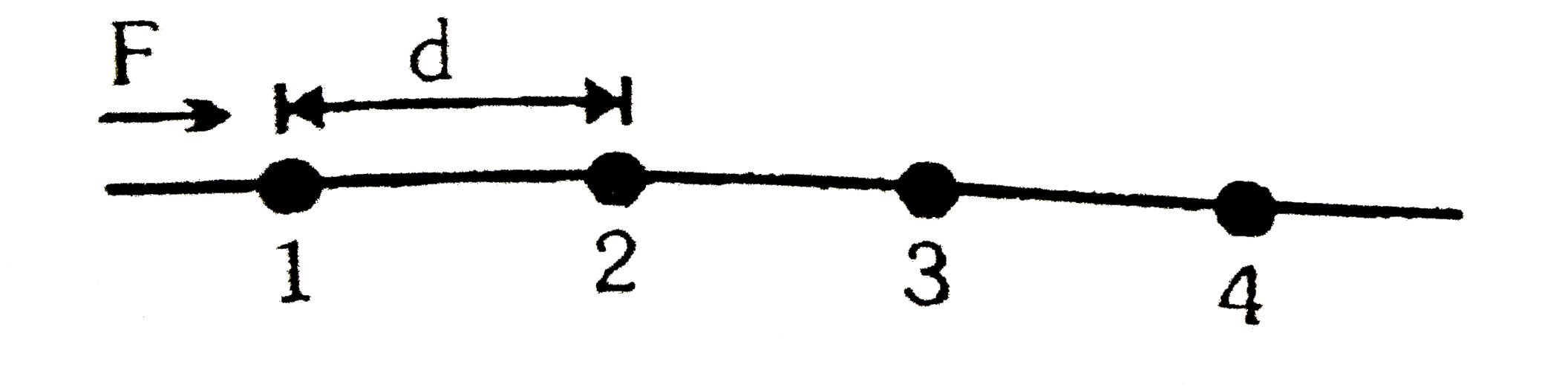
- The Fig. showns a string of equally placed beads of mass m, separated ...
Text Solution
|
- Two persons A and B of weight 80 kg and 50 kg respectively are standin...
Text Solution
|
- In a one dimensional collision between two identical particles A and B...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls of same mass are dropped from the same height onto the floor...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball falling vertically downward with constant velocity 4m//s ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 4m which is at rest explodes into four equal fragme...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shown the velocity as a function of the time for an object ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle mass m = 0.1 kg is released from rest from a point A of a w...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 1kg is suspended by an inextensible string 1m long atta...
Text Solution
|
- Find the distance between centre of gravity and centre of mass of a tw...
Text Solution
|
- After calling a wall of 3 m heigh a mass of weight W drops himself to ...
Text Solution
|
- An open water tight railway wagon of mass 5 xx 10(3) kg coats at an in...
Text Solution
|
- Three blocks A, B and C each of mass m are placed on a surface as show...
Text Solution
|
- Two masses A and B of mass M and 2M respectively are connected by a co...
Text Solution
|
- A disk A of radious r moving on perfectly smooth surface at a speed v ...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical ball of mass 1 kg moving with a uniform speed of 1 m//s co...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth sphere A of mass m collides elastically with an identical sph...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moving with kinetic energy = 3J makes an elastic head-on co...
Text Solution
|