Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
LIMITS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Numerical Value Type|26 VideosLIMITS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Archives JEE MAIN|8 VideosLIMITS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Linked Comprehension Type|20 VideosJEE 2019
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Chapter 10|8 VideosLINEAR COMBINATION OF VECTORS, DEPENDENT AND INDEPENDENT VECTORS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise DPP 1.2|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PUBLICATION-LIMITS-Matrix Match Type
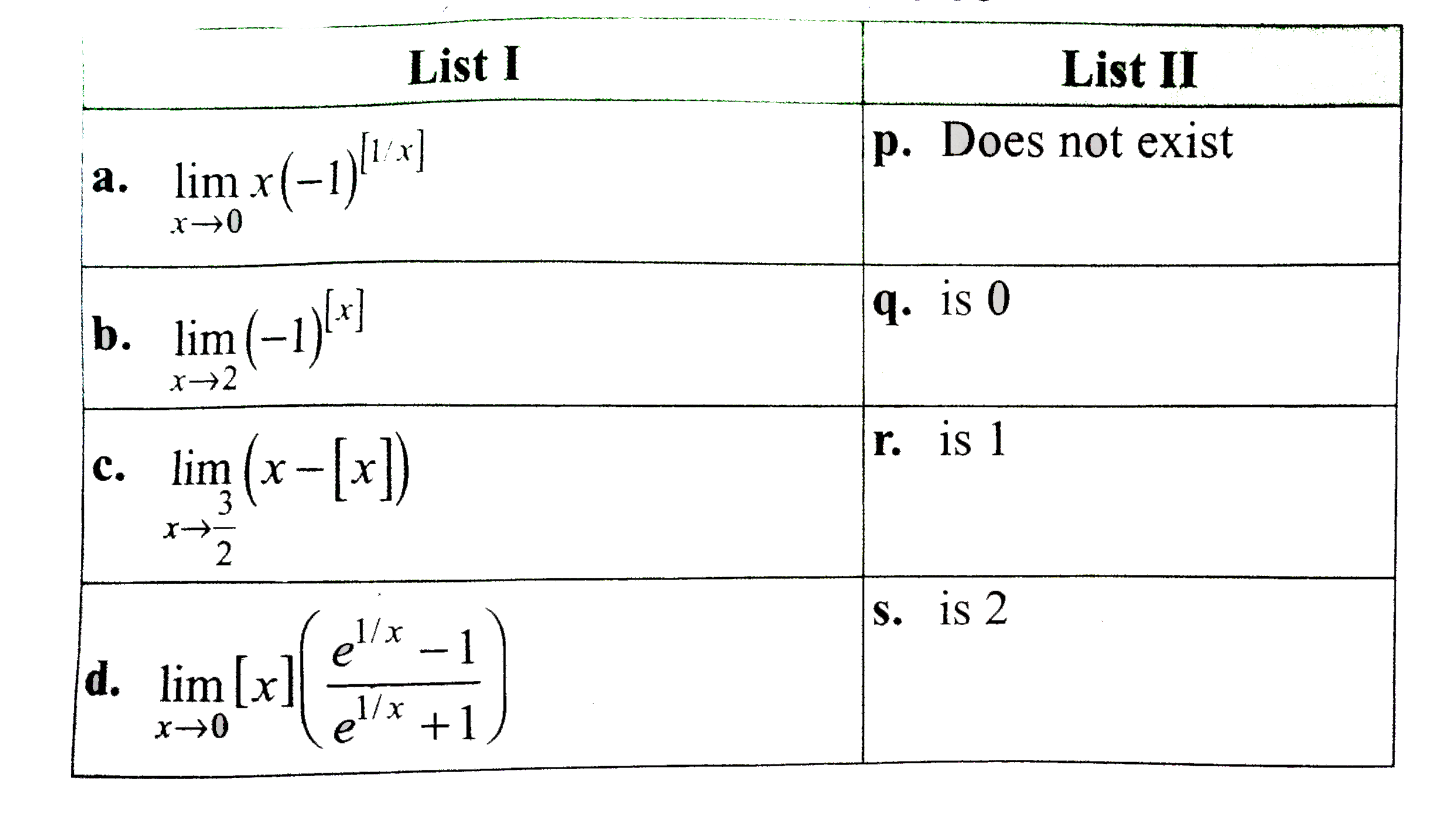
- Match the following lists:
Text Solution
|
- Factorise the expression: am^2+bm^2+bn^2+an^2
Text Solution
|
- Compute lim x → − 2 ( 3 x 2 + 5 x − 9 )
Text Solution
|
- Consider lim(x to oo)((x^(3)+x^(2)+x+sinx)/(x^(2)+2cosx)-asinx-bx+c)=4...
Text Solution
|
- Match the following lists (where [x] represents the greatest integer f...
Text Solution
|