A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
COORDINATE SYSYEM
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Matrix match type|4 VideosCOORDINATE SYSYEM
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Numerical value|12 VideosCOORDINATE SYSYEM
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Multiple correct|13 VideosCOORDINATE SYSTEM
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Multiple Correct Answers Type|2 VideosCROSS PRODUCTS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise DPP 2.2|13 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PUBLICATION-COORDINATE SYSYEM -Linked
- For points P=(x1,y1)and Q =(x2,y2) of the co-ordinate plane a new dist...
Text Solution
|
- For points P-=(x1y1) and Q-=(x2,y2) of the coordinate plane, a new dis...
Text Solution
|
- For points P=(x1,y1)and Q =(x2,y2) of the co-ordinate plane a new dist...
Text Solution
|
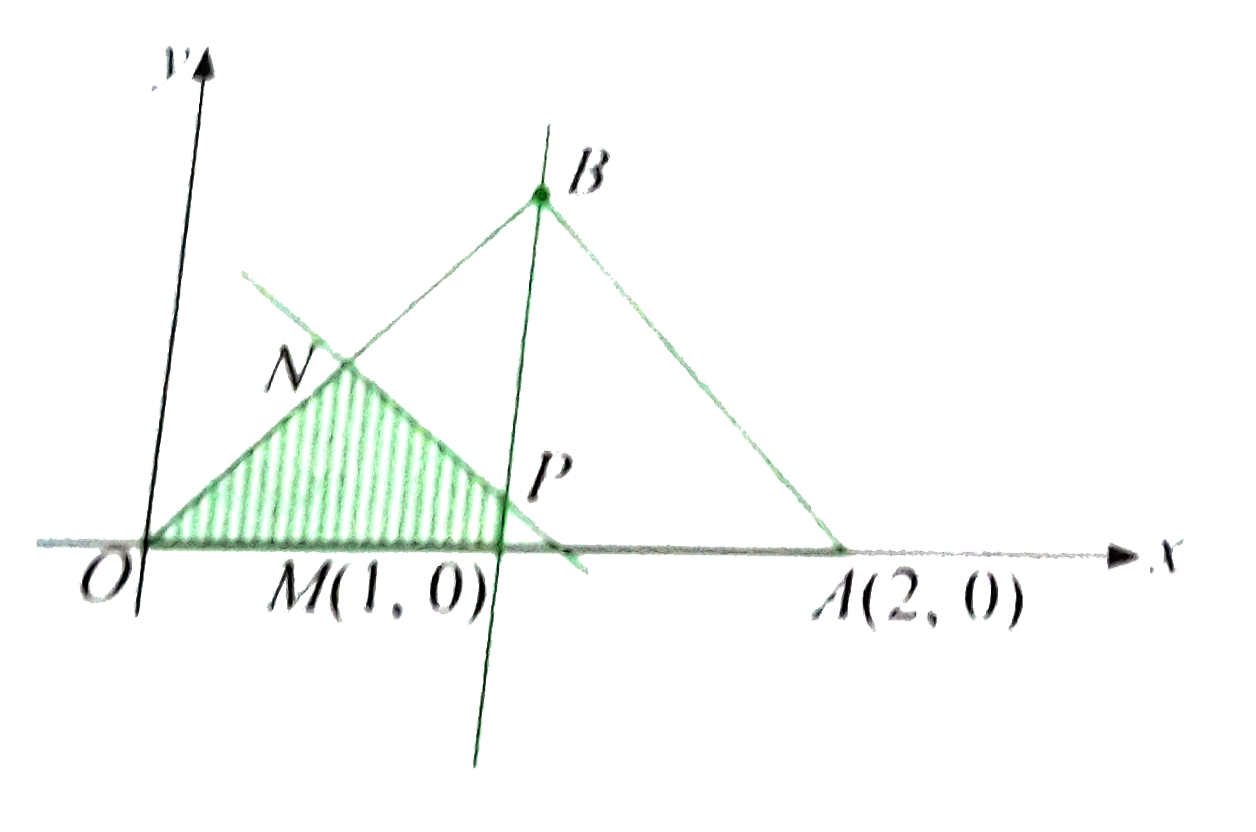
- Let O(0,0),A(2,0),a n dB(1, 1/(sqrt(3))) be the vertices of a triangle...
Text Solution
|
- Let O(0,0),A(2,0),a n dB(1, 1/(sqrt(3))) be the vertices of a triangle...
Text Solution
|
- Let ABCD is a square with sides of unit length. Points E and F are tak...
Text Solution
|
- Let ABCD be a square with sides of unit lenght. Points E and F are tak...
Text Solution
|
- Let ABCD be a square with sides of unit lenght. Points E and F are tak...
Text Solution
|
- Let ABC be an acute- angled triangle and AD, BE, and CF be its medians...
Text Solution
|
- Let ABC be an acute- angled triangle and AD, BE, and CF be its medians...
Text Solution
|