A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
PROPERTIES AND SOLUTIONS OF TRIANGLE
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Matrix match type|6 VideosPROPERTIES AND SOLUTIONS OF TRIANGLE
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Numerical value type|22 VideosPROPERTIES AND SOLUTIONS OF TRIANGLE
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Multiple correct answer type|24 VideosPROGRESSION AND SERIES
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise ARCHIVES (NUMERICAL VALUE TYPE )|8 VideosRELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise All Questions|1119 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PUBLICATION-PROPERTIES AND SOLUTIONS OF TRIANGLE-Linked comprehension type
- An isosceles triangle has two equal sides of length 'a' and angle betw...
Text Solution
|
- Incircle of DeltaABC touches the sides BC, AC and AB at D, E and F, re...
Text Solution
|
- Incircle of DeltaABC touches the sides BC, AC and AB at D, E and F, re...
Text Solution
|
- Incircle of DeltaABC touches the sides BC, AC and AB at D, E and F, re...
Text Solution
|
- Bisectors of angles A, B and C of a triangle ABC intersect its circum...
Text Solution
|
- Internal bisectors of DeltaABC meet the circumcircle at point D, E, an...
Text Solution
|
- Internal bisectors of DeltaABC meet the circumcircle at point D, E, an...
Text Solution
|
- The area of any cyclic quadrilateral ABCD is given by A^(2) = (s -a) (...
Text Solution
|
- The area of any cyclic quadrilateral ABCD is given by A^(2) = (s -a) (...
Text Solution
|
- The area of any cyclic quadrilateral ABCD is given by A^(2) = (s -a) (...
Text Solution
|
- In DeltaABC, R, r, r(1), r(2), r(3) denote the circumradius, inradius,...
Text Solution
|
- In DeltaABC, R, r, r(1), r(2), r(3) denote the circumradius, inradius,...
Text Solution
|
- In DeltaABC, R, r, r(1), r(2), r(3) denote the circumradius, inradius,...
Text Solution
|
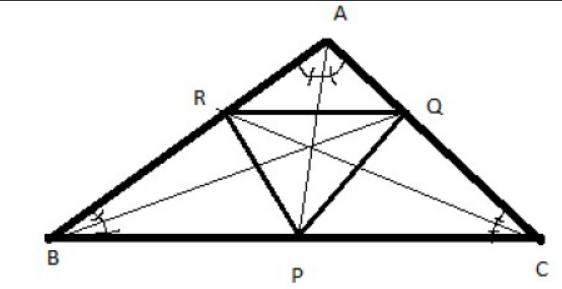
- In DeltaABC, P,Q, R are the feet of angle bisectors from the vertices ...
Text Solution
|
- In triangleABC, P,Q, R are the feet of angle bisectors from the vertic...
Text Solution
|
- Let G be the centroid of triangle ABC and the circumcircle of triangle...
Text Solution
|
- Let G be the centroid of triangle ABC and the circumcircle of triangle...
Text Solution
|
- Let G be the centroid of triangle ABC and the circumcircle of triangle...
Text Solution
|
- The inradius in a right angled triangle with integer sides is r If r...
Text Solution
|
- The inradius in a right angled triangle with integer sides is r If r...
Text Solution
|