Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise example|10 VideosTRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Concept Application Exercises 2.1|8 VideosTRIGONOMETRIC EQUATIONS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Archives (Numerical value type)|4 VideosTRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS AND TRANSFORMATION FORMULAS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Archives (Numerical Value Type)|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PUBLICATION-TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS -SINGLE CORRECT ANSWER TYPE
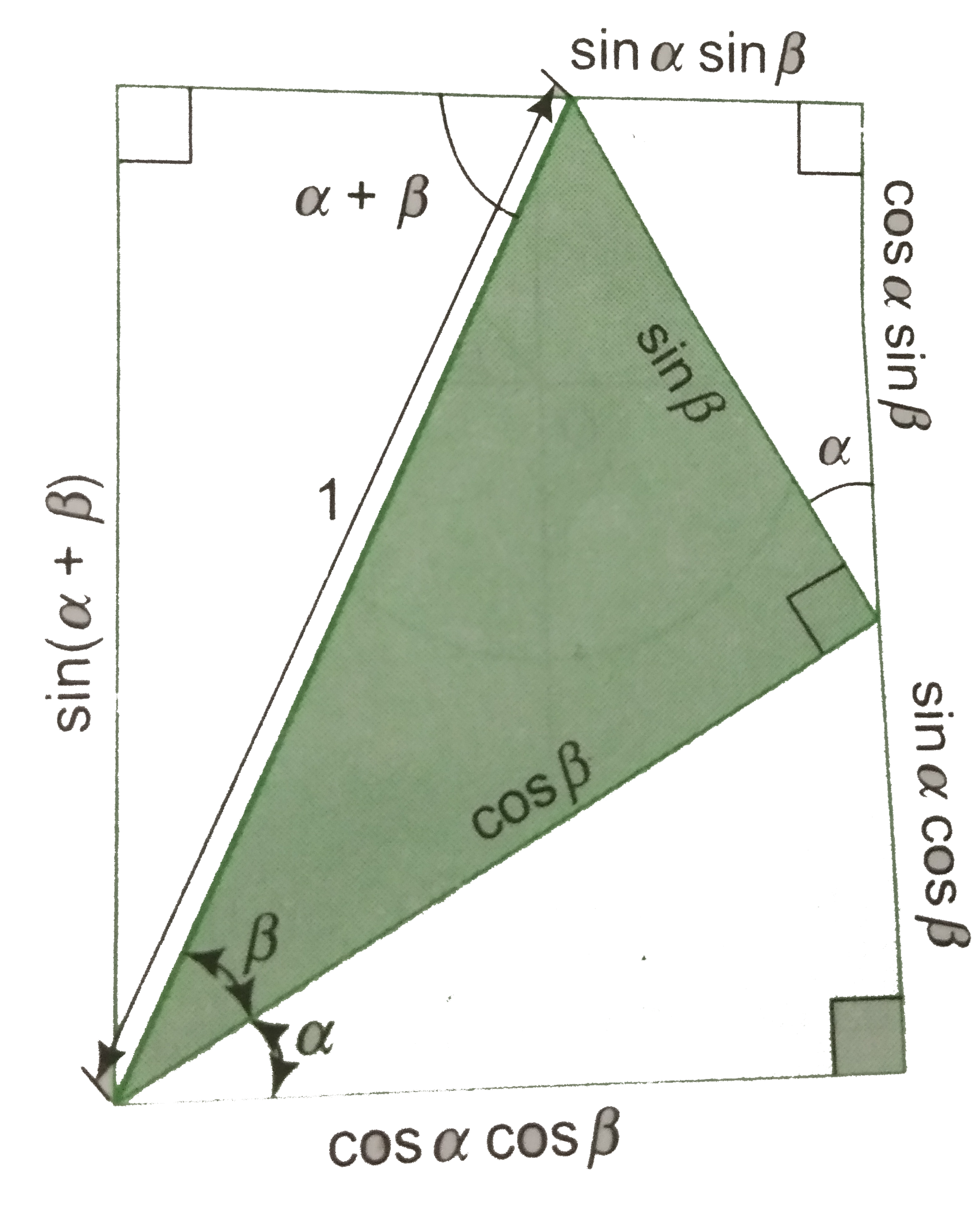
- By geometrical interpretation, prove that sin(alpha+beta)s inalphaco...
Text Solution
|
- The circular wire of diameter 10 cm is cut and placed along the circum...
Text Solution
|
- Find the cartesian co-ordinates of the points whose polar co-ordinates...
Text Solution
|
- If theta in (pi//4, pi//2) and sum(n=1)^(oo)(1)/(tan^(n)theta)=sin the...
Text Solution
|
- Find the cartesian co-ordinates of the points whose polar co-ordinates...
Text Solution
|
- Find the cartesian co-ordinates of the points whose polar co-ordinates...
Text Solution
|
- Find the cartesian co-ordinates of the points whose polar co-ordinates...
Text Solution
|
- If (sin^(2)x-2cos^(2)x+1)/(sin^(2)x+2cos^(2)x-1)=4, then the value of ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the cartesian co-ordinates of the points whose polar co-ordinates...
Text Solution
|
- If tantheta-cottheta=aandsintheta+costheta=b, then, (b^2-1)^2(a^2+4...
Text Solution
|
- The least value of 18 sin^(2)theta+2 cosec^(2)theta-3 is (a) -15 (b) ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the cartesian co-ordinates of the points whose polar co-ordinates...
Text Solution
|
- Find the cartesian co-ordinates of the points whose polar co-ordinates...
Text Solution
|
- Find the cartesian co-ordinates of the points whose polar co-ordinates...
Text Solution
|
- Simplify :cos(x-(pi)/(2)).tan((3pi)/(2)+x)
Text Solution
|
- Consider angles alpha = (2n+(1)/(2))pi pm A and beta = m pi +(-1)^(m)(...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is true ?
Text Solution
|
- If the angle A of a triangle ABC is given by the equation 5 cos A + 3 ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is greatest ?
Text Solution
|
- The number of value/values of x for which sin y=x^(2)-2x si possible i...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is not correct ?
Text Solution
|