A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PUBLICATION-COMPLEX NUMBERS-MULTIPLE CORRECT ANSWER TYPE
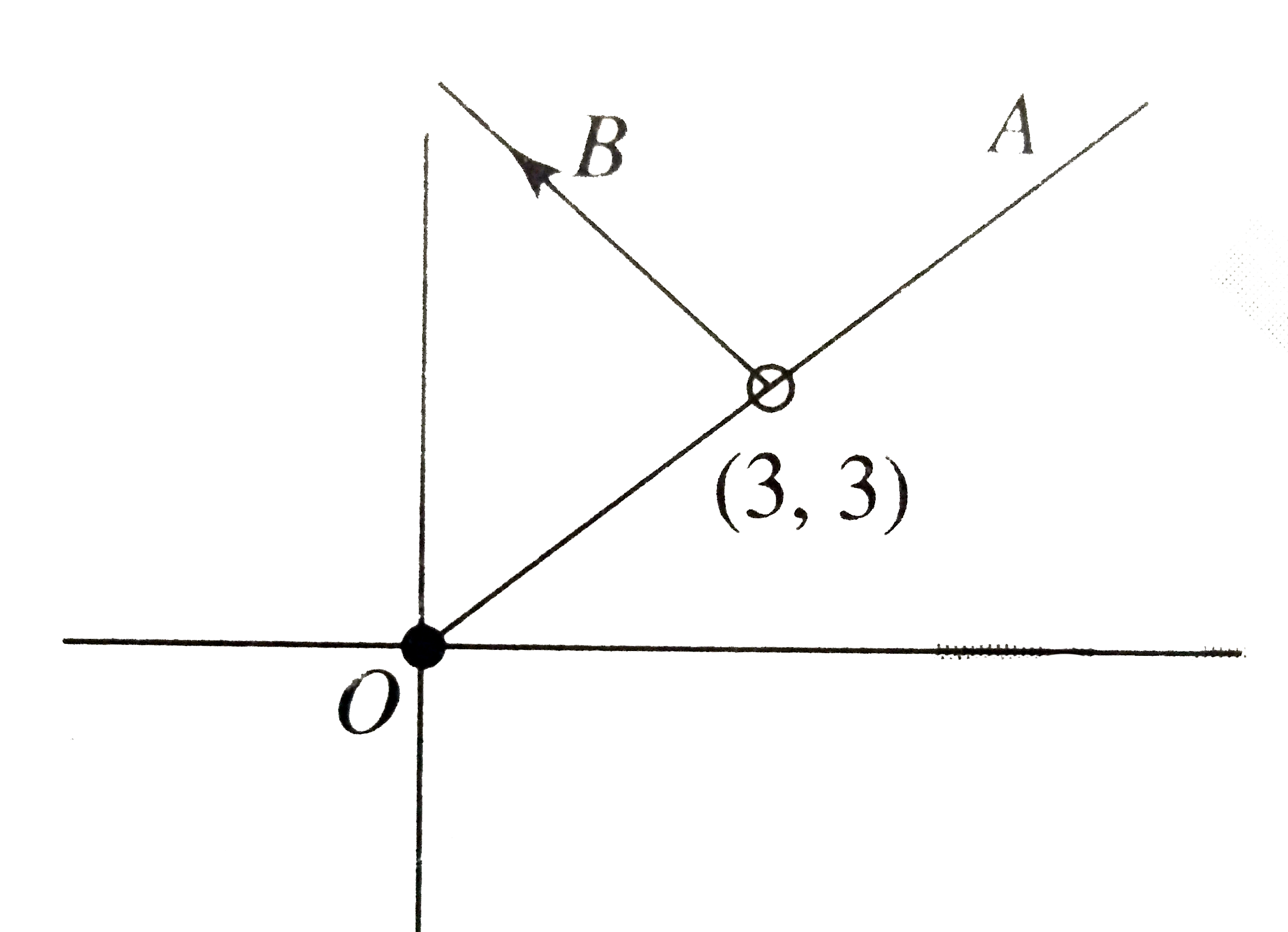
- Let z in C and if A={z:"arg"(z)=pi/4}and B={z:"arg"(z-3-3i)=(2pi)/3}. ...
Text Solution
|
- Let z(1) and z(2) be two distinct complex numbers and z=(1-t)z(1)+tz(2...
Text Solution
|
- about to only mathematics
Text Solution
|
- Let a,b in R and a^(2)+b^(2) ne 0. Suppose S={z in C:z=(1)/(a+ibt),t...
Text Solution
|
- Let a , b ,xa n dy be real numbers such that a-b=1a n dy!=0. If the co...
Text Solution
|
- For a non-zero complex number z , let arg(z) denote the principal ar...
Text Solution
|
- Let s ,\ t ,\ r be non-zero complex numbers and L be the set of ...
Text Solution
|