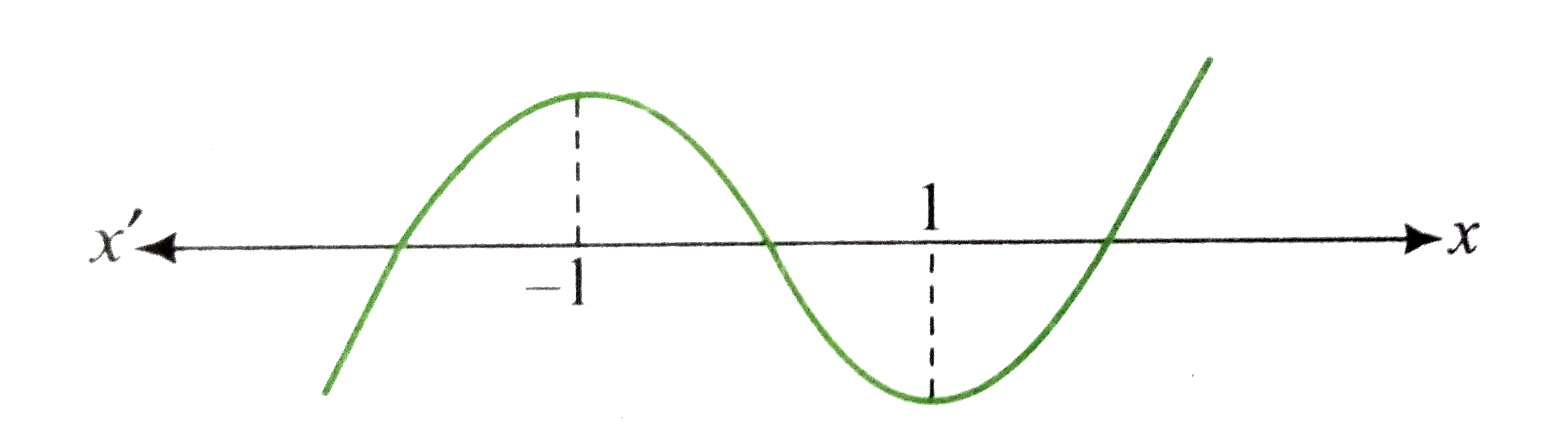
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THEORY OF EQUATIONS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE 2.7|9 VideosTHEORY OF EQUATIONS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE 2.8|11 VideosTHEORY OF EQUATIONS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE 2.5|4 VideosSTRAIGHT LINES
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise ARCHIVES (NUMERICAL VALUE TYPE)|1 VideosTHREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise All Questions|291 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PUBLICATION-THEORY OF EQUATIONS-CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE 2.6
- How many roots of the equation 3x^4+6x^3+x^2+6x+3=0 are real ?
Text Solution
|
- Find the value of a if x^3-3x+a=0 has three distinct real roots.
Text Solution
|
- Analyze the roots of the equation (x-1)^3+(x-2)^3+(x-4)^3+(x-5)^3=0 by...
Text Solution
|
- In how many points the graph of f(x)=x^3+2x^2+3x+4 meets the x axis ?
Text Solution
|