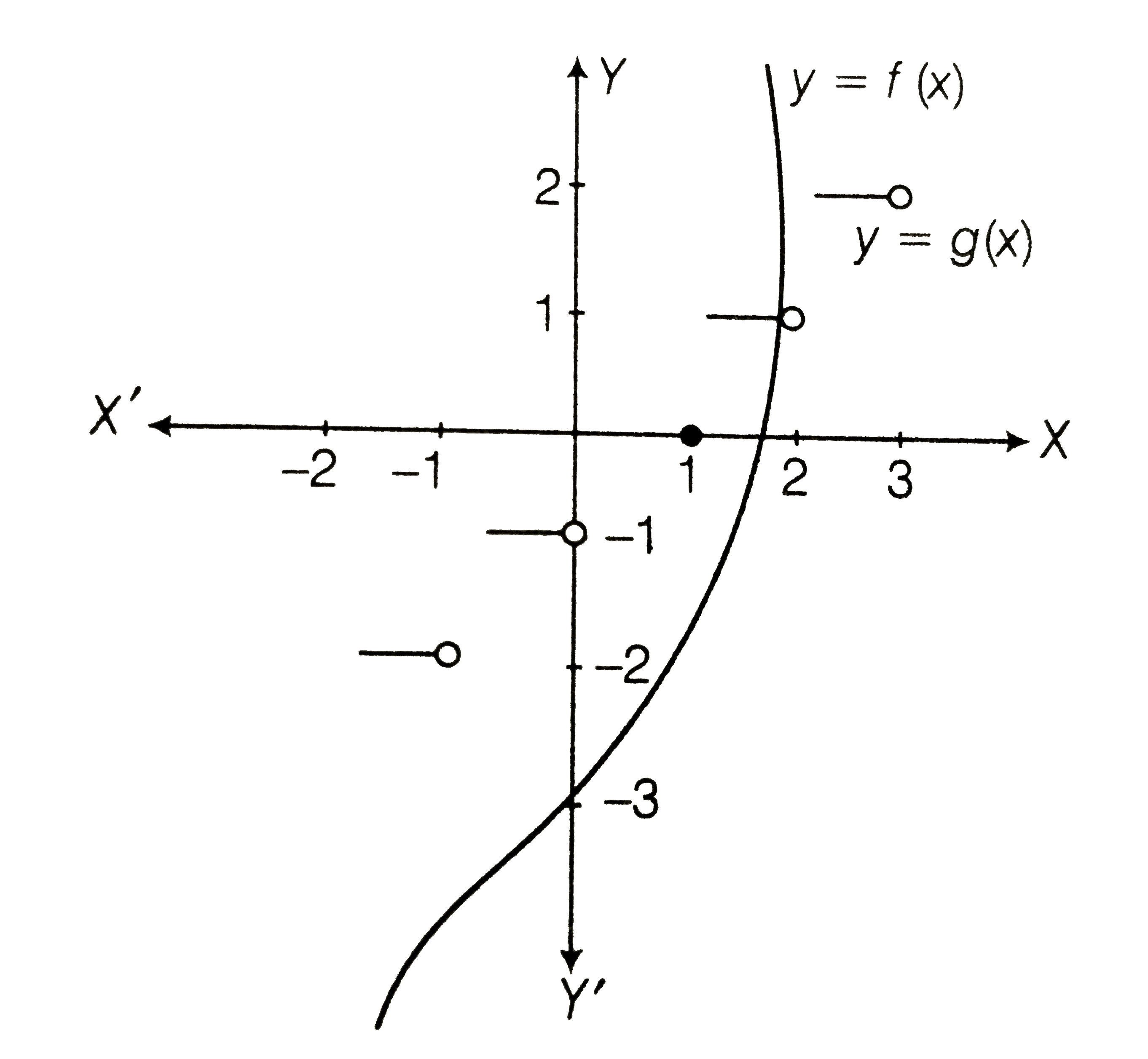
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
THEORY OF EQUATIONS
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise For Session 1|11 VideosTHEORY OF EQUATIONS
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise For Session 2|10 VideosTHE STRAIGHT LINES
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise The Straight Lines Exercise 8 : (Questions Asked in Previous 13 years Exams)|1 VideosTHREE DIMENSIONAL COORDINATE SYSTEM
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Three Dimensional Coordinate System Exercise 12 : Question Asked in Previous Years Exam|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ARIHANT MATHS-THEORY OF EQUATIONS-Exercise (Questions Asked In Previous 13 Years Exam)
- Solve the equation x^(3)-[x]=3, where [x] denotes the greatest integer...
Text Solution
|
- In the quadratic equation ax^2 + bx + c = 0. if delta = b^2-4ac and al...
Text Solution
|
- Let S denote the set of all polynomials P(x) of degree lt=2 such th...
Text Solution
|
- If the roots of x^2-b x+c=0 are two consecutive integers, then b^2-4c ...
Text Solution
|
- If the equation a(n)x^(n)+a(n-1)x^(n-1)+..+a(1)x=0, a(1)!=0, n ge2, ha...
Text Solution
|
- If both the roots of the quadratic equation x^(2)-2kx+k^(2)+k-5=0 are ...
Text Solution
|
- Let a and b be the roots of the equation x^2-10 c x-11 d=0 and those ...
Text Solution
|
- Let a,b,c be the sides of a triangle. No two of them are equal and lam...
Text Solution
|
- All the value of m for which both the roots of the equation x 2 −2mx...
Text Solution
|
- If the roots of the quadratic equation x^2+p x+q=0 are tan30^0a n dtan...
Text Solution
|
- Let alpha,beta be the roots of the equation x^2-p x+r=0a n dalpha//2,2...
Text Solution
|
- If the difference between the roots of the equation x^2+a x+1=0 is les...
Text Solution
|
- Let a ,b , c ,p ,q be real numbers. Suppose alpha,beta are the roots o...
Text Solution
|
- The quadratic equations x^2""-6x""+""a""=""0""a n d ""x^2""-c x""+""...
Text Solution
|
- How many real solutions does the equation x^7+14 x^5+16 x^3+30 x-560=0...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose the cubic x^(3)-px+q has three distinct real roots, where pgt0...
Text Solution
|
- Find the discriminant of the quadratic equation 2x^2-4x+3=0, and hence...
Text Solution
|
- If the roots of the equation b x^2+""c x""+""a""=""0 be imaginary, t...
Text Solution
|
- Let p and q real number such that p!= 0,p^3!=q and p^3!=-q. if alpha a...
Text Solution
|
- solve 0=-1+2x+3x^2
Text Solution
|
- Find the roots of x^2-6x-2=0
Text Solution
|