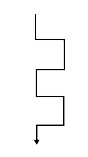
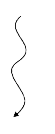
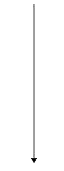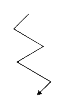A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KVPY PREVIOUS YEAR-QUESTION PAPER 2013-PART-II ( PHYSICS)
- A man inside a freely falling box throws a heavy ball towards a side w...
Text Solution
|
- A bullet of mass m is fired horizontally into a large sphere of mass M...
Text Solution
|
- A small boy is throwing a ball towards a wall 6 in front of him. He r...
Text Solution
|
- In the P-V diagram below the dashed curved line is an adiabat. Fo...
Text Solution
|
- A singly ionized helium atom in an excited state (n = 4) emits a photo...
Text Solution
|
- The figure below shows a circuit and its input voltage v(i) as functio...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is rolling without slipping in a spherical shallow bowl (radius...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere rolls without slipping, first horizontal and then up to...
Text Solution
|
- The three processes in a thermodynamic cycle shown in the figure are :...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m slides from rest at a height H on a frictionless inc...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic prong consists of 4 rods made of the same material, cross-s...
Text Solution
|