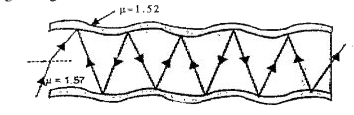
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
REFRACTION OF LIGHT
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|9 VideosREFRACTION OF LIGHT
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise NUMERICAL PROBLEMS|36 VideosREFRACTION OF LIGHT
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise MOST EXPECTED QUESTIONS|2 VideosREFLECTION OF LIGHT
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise NUMERICALS PROBLEMS|7 VideosSEMI CONDUCTOR DEVICES
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise Most Expected Questions|6 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION-REFRACTION OF LIGHT-SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
- What is meant by power of a lens? What does its sign indicate? State i...
Text Solution
|
- Why diamond is hard while graphite is soft ?
Text Solution
|
- Write the conditions for total internal reflection to takeplace?
Text Solution
|
- How will you explain twinkling of stars?
Text Solution
|
- When does snell's law in refraction fails?
Text Solution
|
- The sun appears red at sun rise or sunset, why?
Text Solution
|
- A concave mirror and a convex lens are held separetly in water. What c...
Text Solution
|
- Answer the following questions: A diver under water, looks obliquely ...
Text Solution
|
- Write the conditions for total internal reflection to takeplace?
Text Solution
|
- Derive the expression for the power of two thin lenses placed in conta...
Text Solution
|
- Explain total internal reflection. What are its conditions?
Text Solution
|
- Prove the relation ""^(a)mu(b)=1/(""^(b)mu(a))
Text Solution
|
- State generalized Snell's law of refraction through multiple parallel ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain total internal reflection. What are its conditions?
Text Solution
|
- Write the conditions for total internal reflection to takeplace?
Text Solution
|
- State the condition of total internal reflection. Calculate the speed...
Text Solution
|
- What are opiates? Give their functions.
Text Solution
|
- What is the relation between critical angle and refractive index? What...
Text Solution
|
- What are the uses of optical fibre?
Text Solution
|