Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SOLUTIONS
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise Question Bank (2 .5 Ideal and non - ideal solutions)|11 VideosSOLUTIONS
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise Question Bank (2 .6 Colligative Properties And Determination of Molar Mass)|28 VideosSOLUTIONS
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise Question Bank (2 .3 Solubility)|8 VideosPOLYMERS
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise QUESTIONS |42 VideosSTRUCTURE OF ATOM
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise NUMERICAL PROBLEMS |6 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION-SOLUTIONS-Question Bank (2 .4 Vapour Pressure of Liquid Solutions)
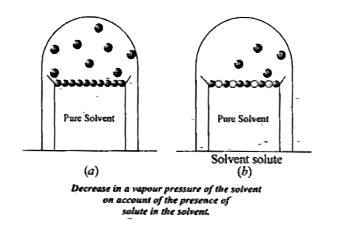
- (a) Define vapour pressure (b) Explain why vapour pressure of a s...
Text Solution
|
- Why the vapour pressure of saline solutions is lower than that of pu...
Text Solution
|
- Why the vapour pressure of a solution of glucose in water is lower tha...
Text Solution
|
- State and explain : Raoult's law for volatile solute.
Text Solution
|
- State and explain : Raoult's law for non-volatile solute.
Text Solution
|
- What are limitations of Raoult's law
Text Solution
|
- Why petrol evaporate faster than water ?
Text Solution
|
- Why is the vapour pressure of a solvent lowered on the addition of ...
Text Solution
|
- Write similarity between Raoult's law and Henry's law
Text Solution
|