Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-EXERCISE - 04 (B)
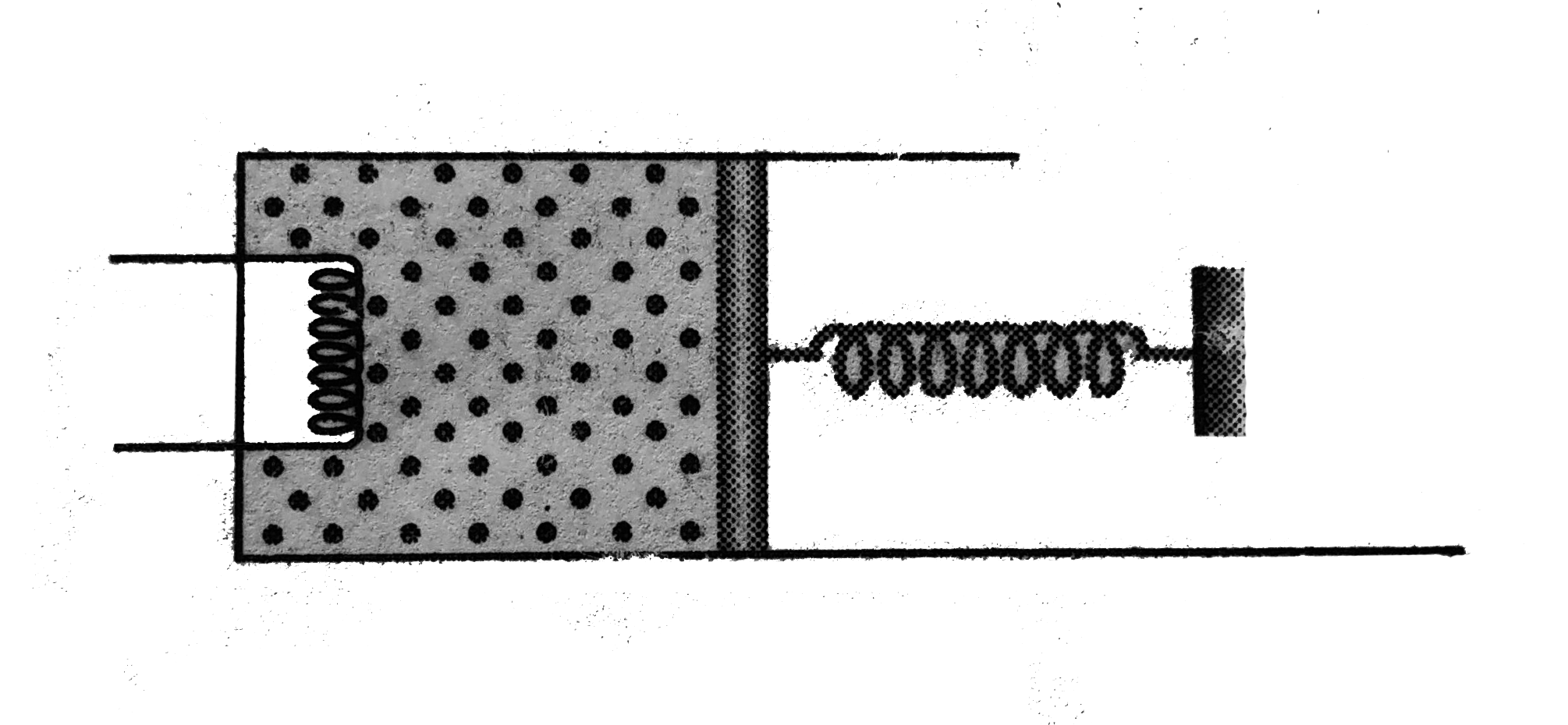
- The rectangular box shown in Fig has partition which can slide without...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal monoatomic gas is confined by a spring loaded massless piston...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical block of length 0.4 m and area of cross-section 0.04 m^2...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a diatomic ideal gas (gamma = 1.4) is taken through a cyc...
Text Solution
|
- The apparatus shown in the figure consists of four glass column connec...
Text Solution
|
- A double-plane window consists of two glass sheets each of area ...
Text Solution
|
- Two spherical flasks having total volume V(0) = 1.0 L containing air a...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of an ideal non linear triatomic gas has a pressure P(0) and ...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of an ideal monoatomic gas are confined within a cylinder by...
Text Solution
|
- A weightless piston divides a thermally insulated cylinder into two pa...
Text Solution
|
- Two vertical cylinders are connected by a small tube at the bottom. It...
Text Solution
|
- A barometer is faulty . When the true barometer reading are 73 cm and ...
Text Solution
|
- A non-conducting cylindrical vessel of length 3l is placed horizontly ...
Text Solution
|
- An op-amp has differential gain Ad=10 .common mode voltage applied to ...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal diatomic gas (gamma=7/5) undergoes a process in which its int...
Text Solution
|