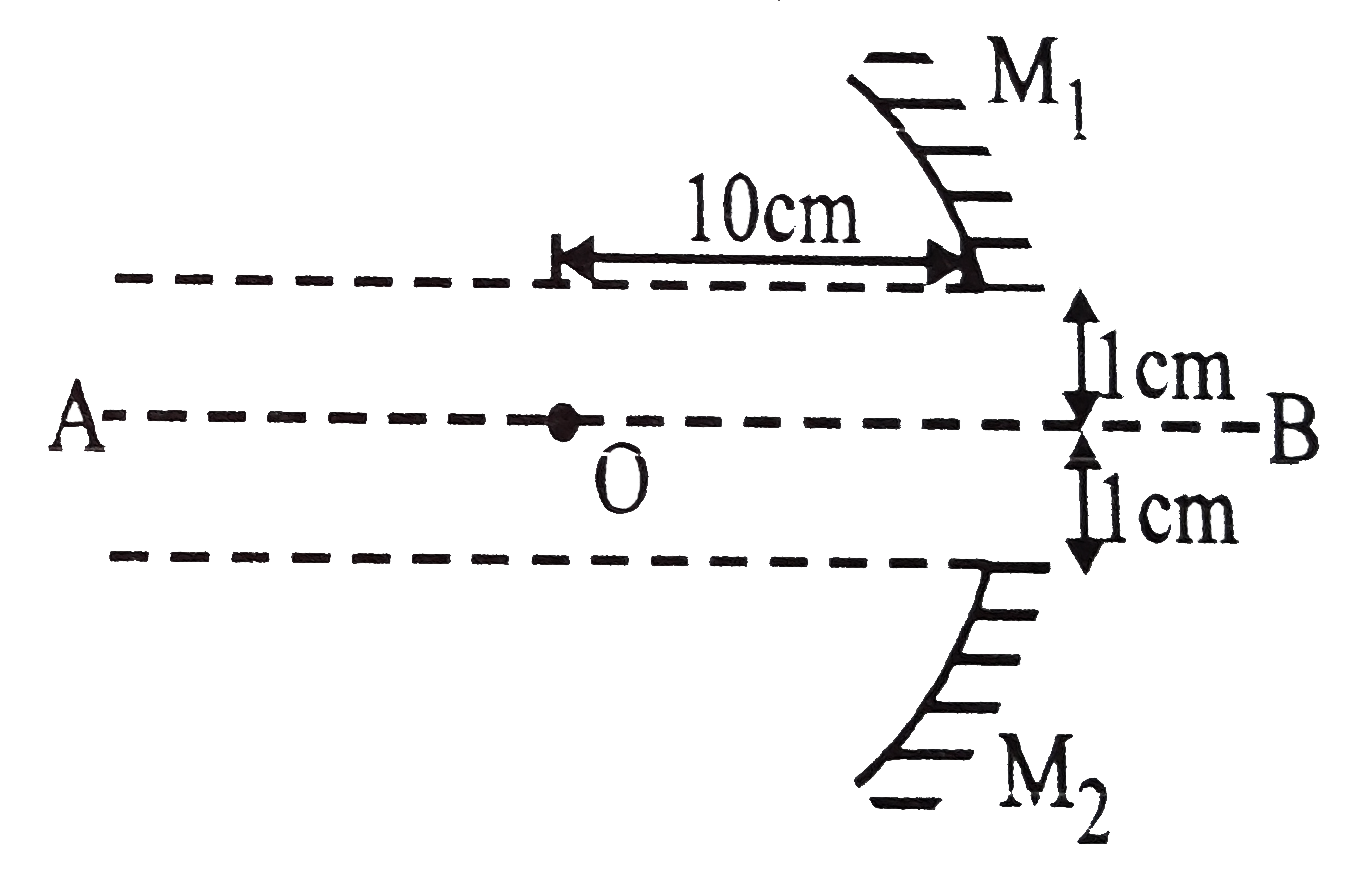A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-EXERCISE- 01
- In the figure shown, how many images of the star will an observer at O...
Text Solution
|
- The distance of an object from a concave spherical mirror is equal to ...
Text Solution
|
- A concave mirror of focal length 20 cm is cut into two parts from the ...
Text Solution
|
- Radius of curvature of each mirror is R. 'O' is object. Consider first...
Text Solution
|
- A convex mirror of focal length 'f' is placed at the origin with its r...
Text Solution
|
- The x-z plane separates two media A and B of refractive indices mu(1) ...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light travelling in a medium of refractive index mu is incide...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in figure. Water (mu(w) = (4)/(3)) is fil...
Text Solution
|
- A plane mirror is placed at the bottom of a tank containing a liquid o...
Text Solution
|
- When a pin is moved along the principal axis of a small concave mirror...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light (R(1)) is incident on a glass slab at an angle equal to...
Text Solution
|
- Refractive index of a glass cube is sqrt(2). A ray of light is inciden...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light travels from an optically denser to rarer medium. The c...
Text Solution
|
- The distance of final image from AB as observed by observer is P is
Text Solution
|
- What is the least radius through which an optical fiber of core diamet...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light from a denser medium strikes a rarer medium at an angle...
Text Solution
|
- An object is immersed in a fluid.In order that the object becomes invi...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident upon an air/water interface ( it passes fro...
Text Solution
|
- A light ray is incident on a transparent sphere of index = sqrt(2) , a...
Text Solution
|
- An air bubble inside water. The refractive index of water is 4/3 . At ...
Text Solution
|