Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-MCQ
- A ray of light travelling in a transparent medium falls on a surface s...
Text Solution
|
- A ray OP of monochromatice light is incident on the face AB of prism ...
Text Solution
|
- A transparent with film of uniform thickness and refractive index n(1)...
Text Solution
|
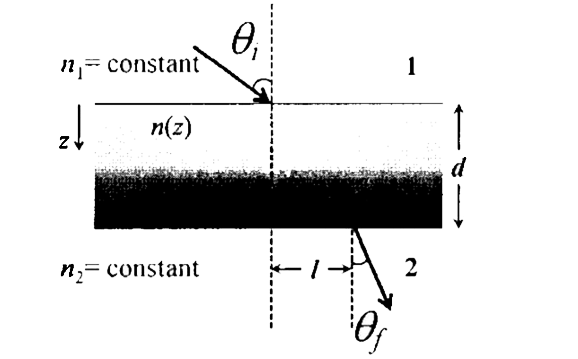
- A transparent slab of thickness d has a refractive index n(z) that inc...
Text Solution
|
- A plano-covex lens is made of a material of refractive index n. When a...
Text Solution
|