Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-subjective
- A prism of refractive index n(1) & another prism of reactive index n(2...
Text Solution
|
- The XY plane is the boundary between two tranparednt media. Medium 1 w...
Text Solution
|
- A quarter culinder fo radius R and refractive index 1.5 is placed o...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens of focal length 15cm and a concave mirror of focal lengt...
Text Solution
|
- The refractive indices of the crown flass for the blue and red lights ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure, light is incident on a thin lens as shown. The radius o...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows an irregular block of material of refractive indec sqrt(2...
Text Solution
|
- An object is approaching a convex lens of focal length 0.3m with a spe...
Text Solution
|
- AB and CD are two slabs. The medium between the slabs has refractive i...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident on a prism ABC of mu = sqrt(3) as shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- The focal length of a thin biconvex lens is 20cm. When an object is mo...
Text Solution
|
- Image of an object approaching a convex mirror of radius of curvature ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a concave mirror and convex lens (refractive index = 1.5 ) of...
Text Solution
|
- A monochromatic beam of light is incided at 60^(@) in one face of an e...
Text Solution
|
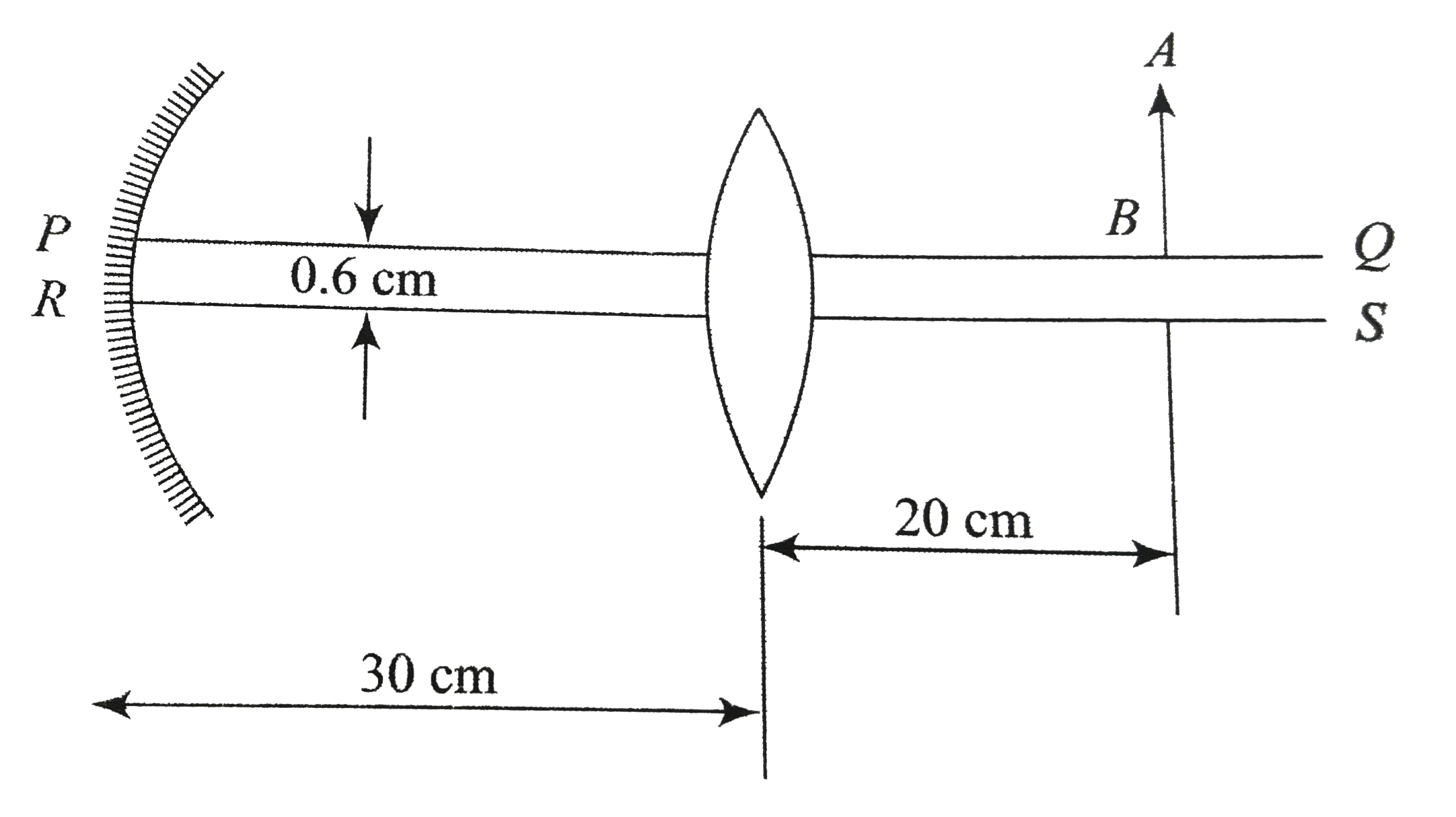
_E01_247_S01.png)
_E01_247_S02.png)