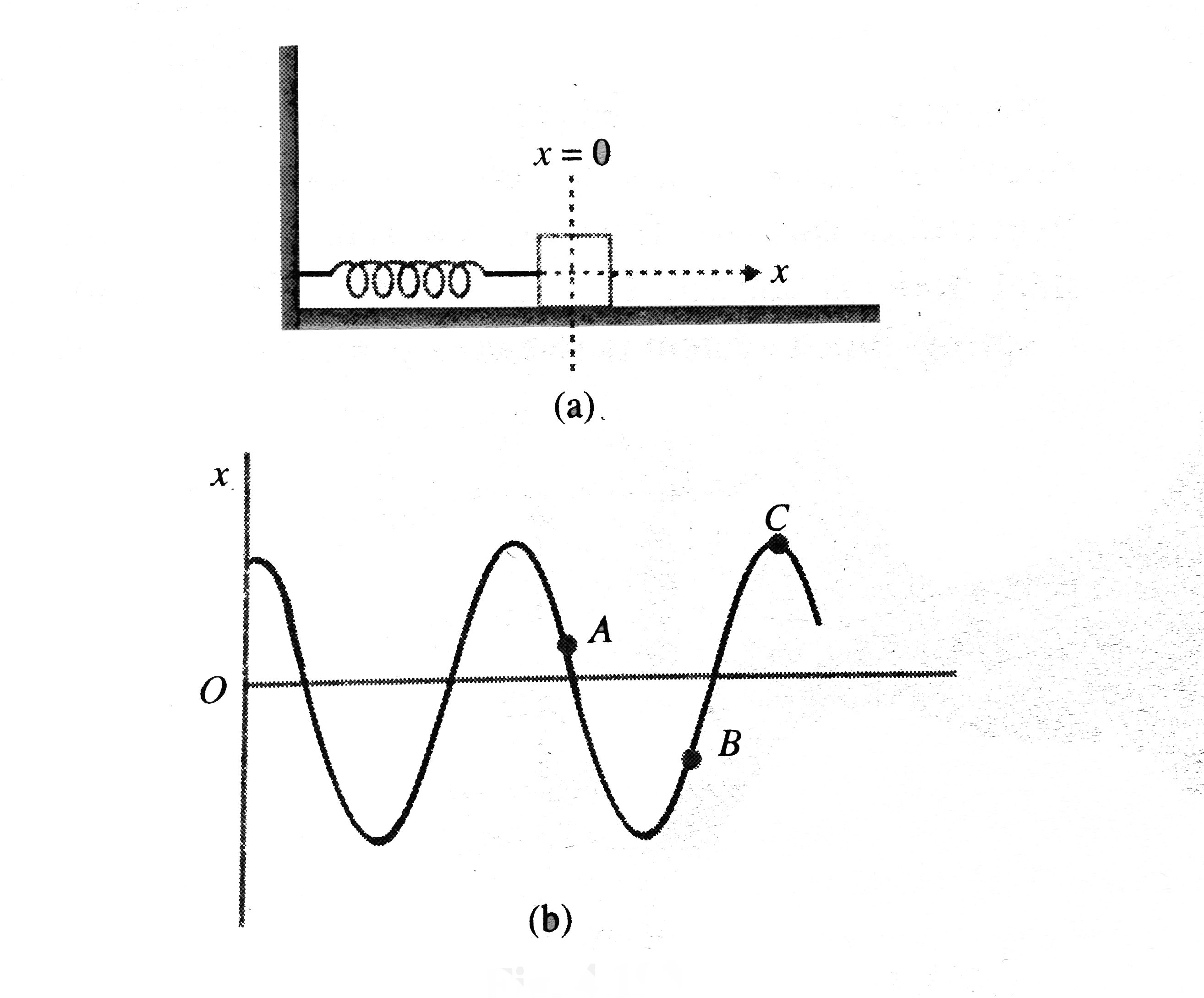
A 100 g block is connected to a horizontal massless spring of force constant `25.6(N)/(m)` As shown in Fig. the block is free to oscillate on a horizontal frictionless surface. The block is displaced 3 cm from the equilibrium position and , at `t=0`, it is released from rest at `x=0` It executes simple harmonic motion with the postive x-direction indecated in Fig. The position time `(x-t)` graph of motion of the block is as shown in Fig.
Q. When the block is at position B on the graph its.
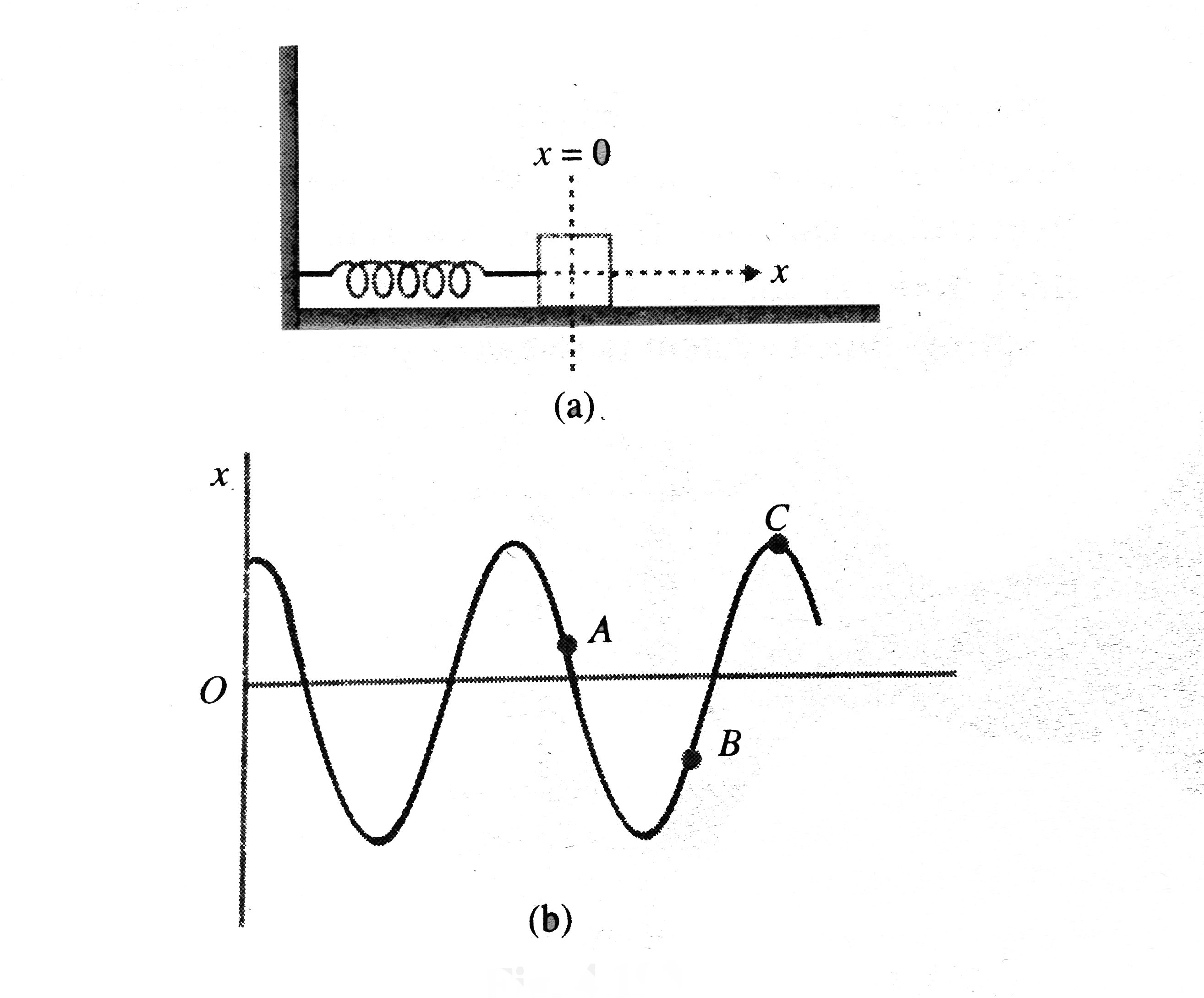
A 100 g block is connected to a horizontal massless spring of force constant `25.6(N)/(m)` As shown in Fig. the block is free to oscillate on a horizontal frictionless surface. The block is displaced 3 cm from the equilibrium position and , at `t=0`, it is released from rest at `x=0` It executes simple harmonic motion with the postive x-direction indecated in Fig. The position time `(x-t)` graph of motion of the block is as shown in Fig.
Q. When the block is at position B on the graph its.
A
position and velocity both are negative
B
position and velocity both are positive.
C
position is negative and velocity is positive.
D
position is positive and velocity is negative.
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
D
At position B, x is positive and `(dx)/(dt)` is negative.
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A 100 g block is connected to a horizontal massless spring of force constant 25.6(N)/(m) As shown in Fig. the block is free to oscillate on a horizontal frictionless surface. The block is displaced 3 cm from the equilibrium position and , at t=0 , it is released from rest at x=0 It executes simple harmonic motion with the postive x-direction indecated in Fig. The position time (x-t) graph of motion of the block is as shown in Fig. Velocity of the block as a function of time can be expressed as
A 100g block is connected to a horizontal massless spring of force constant 25.6 N//m . The block is free to oscillate on a horizontal fricationless surface. The block is displced by 3 cm from the equilibrium position, and at t = 0 , it si released from rest at x = 0 , The position-time graph of motion of the block is shown in figure. When the block is at position A on the graph, its
A 100g block is connected to a horizontal massless spring of force constant 25.6 N//m . The block is free to oscillate on a horizontal fricationless surface. The block is displced by 3 cm from the equilibrium position, and at t = 0 , it si released from rest at x = 0 , The position-time graph of motion of the block is shown in figure. Let us now make a slight change to the initial conditions. At t = 0 , let the block be released from the same position with an initial velocity v_(1) = 64 cm//s . Position of the block as a function of time can be expressed as
A 10 kg mass is connected at one end of a massless spring with force constant k = 1000 N/m, keeping other end fixed in a horizontal plane as shown in the fig. 15.6 If the sytem is displaced by 0.01 m from its equilibrium position A to a point B, then the acceleration of the system is
A small block is connected to one end of a massless spring of un - stretched length 4.9 m . The other end of the spring (see the figure) is fixed. The system lies on a horizontal frictionless surface. The block is stretched by 0.2 m and released from rest at t = 0 . It then executes simple harmonic motion with angular frequency (omega) = (pi//3) rad//s . Simultaneously at t = 0 , a small pebble is projected with speed (v) from point (P) at an angle of 45^@ as shown in the figure. Point (P) is at a horizontal distance of 10 m from O . If the pebble hits the block at t = 1 s , the value of (v) is (take g = 10 m//s^2) . .
A small block is connected to one end of a massless spring of un-stretched length 4.9 m. The other end of the spring (see the figure) is fixed. The system lies on a horizontal frictionless surface. The block is stretched by 0.2 m and released from rest at t = 0. It then executes simple harmonic motion with angular frequency omega = (pi)/(3) rad/s . Simultaneously at t = 0, a small pebble is projected with speed nu from point P at an angle of 45^(@) as shown in the figure. Point P is at a horizontal distance of 10 m from O. If the pebble hits the block at t = 1s, the value of nu is (take g = 10 m/ s^(2) )
A block of mass m is attached to four unstretched massless springs of spring constant k_1 and k_2 as shown in figure. The block is displaced towards right through distance x and is released. Speed of block when displacement of block is x/2 from mean position is :
A block of mass m hangs from a vertical spring of spring constant k. If it is displaced from its equilibrium position, find the time period of oscillations.
A block of mass m is connected with two ideal pullies and a massless spring of spring constant K as shown in figure. The block is slightly displaced from its equilibrium position. If the time period of oscillation is mupisqrt(m/K) . Then find the value of mu .
A 2 kg block is connected with two springs of force constants k_(1)=100 N//m and k_(2)=300 N//m as shown in figure. The block is released from rest with the springs unstretched. The acceleration of the block in its lowest postion is (g=10 m//s^(2))